Niger State was created on the 3rd February, 1976 out of the then North-Western state during the regime of General Murtala Ramat Mohammed; the state formerly began to function on April 1st of that year, with eight Local Government Councils (LGAs) namely: Chanchaga, Rafi, Gbako, Etswan, Suleja, Mariga, Magama and Lavun. Etswan Local Government was later divided into two (Agaie and Lapai LGAs).

Between 1979 and 1983 during the second republic, when Mallam Muhammadu Awwal Ibrahim was the Executive Governor of the State, eighteen LGAs were created: Kuta, Paikoro, Chanchaga, Rafi, Gbako, Katcha, Lemu, Lapai, Agaie, Suleja, Mariga, Bangi, Magama, Auna, Lavun, Mokwa and Jima-Doko. But when the military came into power in 1984, it was reverted to the original eight LGA structure. However, Chanchaga was split into two-Minna Municipal council, with Minna as headquarters while Kuta remained the headquarters of Shiroro LGA, the former name of Chanchaga LGA.
The LGAs in Niger State became Nineteen (19) in 1991 when President Ibrahim Babangida created Nine (9) States and additional LGAs in Nigeria. By 1996 when Late General Sani Abacha created six (6) additional states and 182 LGAs in the entire country, Niger State got additional six (6) LGAs, namely, Katcha, Munya, Mashegu, Edati, Tafa and Mariga bringing the total to 25 LGAs.
In the year 2002, the Civilian administration of Engr. Abdulkadir A. Kure responded to the clarion call of the people for the creation of additional local government areas. To this end, additional 17 new local government areas were created out of the existing ones; bringing the total number of local governments to 42.
However, because this was not gazetted by the National Assembly as enshrined in the constitution, the new LGAs were dissolved and converted to Area Development Councils. Thus, the status-quo of 25 LGAs was maintained.
List of Local Government Areas
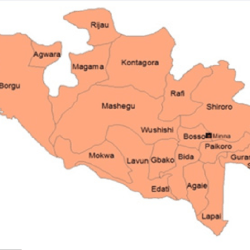
Niger State has 25 Local Government Areas, namely:
- Agaie
- Agwara
- Bida
- Borgu
- Bosso
- Chanchaga
- Edati
- Gbako
- Gurara
- Katcha
- Kontagora
- Lapai
- Lavun
- Magama
- Mariga
- Mashegu
- Mokwa
- Munya
- Paikoro
- Rafi
- Rijau
- Shiroro
- Suleja
- Tafa
- Wushishi
Local Government Areas and their headquarters
The Local Government Areas in Niger State and their headquarters are:
| SN | LGA | HEADQUARTERS |
| 01 | Agaie | Agaie |
| 02 | Agwara | Agwara |
| 03 | Bida | Bida |
| 04 | Borgu | New Bussa |
| 05 | Bosso | Maikunkele |
| 06 | Edati | Enagi |
| 07 | Gurara | Gawu Babangida |
| 08 | Gbako | Lemu |
| 09 | Katcha | Katcha |
| 10 | Kontagora | Kontagora |
| 11 | Lapai | Lapai |
| 12 | Lavun | Kutigi |
| 13 | Mariga | Bangi |
| 14 | Mokwa | Mokwa |
| 15 | Magama | Nasko |
| 16 | Mashegu | Mashegu |
| 17 | Munya | Sarkin Pawa |
| 18 | Paikoro | Paiko |
| 19 | Rafi | Kagara |
| 20 | Rijau | Rijau |
| 21 | Shiroro | Kuta |
| 22 | Suleja | Suleja |
| 23 | Tafa | Sabon-Wuse |
| 24 | Wushishi | Wushishi |
| 25 | Minna | Minna |

Boundaries: Niger State shares its borders with republic of Benin (West), Zamfara State (North), Kebbi (North-West), Kogi (South), Kwara (South West), Kaduna (North-East) and the FCT (South-East).
Land area, the largest among Nigerian states: Niger State is one of the largest states in Nigeria covering about 86,000km2 (or about 8.6million hectares) representing about 9.3% of the total land area of the country.
Major rivers: Niger State’s major rivers are: Niger, Kaduna, Gbako, Eko, Gurara, Ebba, Ega, Mariga and their tributaries.

Fishes: The common fishes found in these rivers are: Nile Perch (Lates) Trunck fish, Cat fish, Osteoglosid, Tilapia, Synodontis, Tiger fish, Moon fish, Mormyrid and Electric fish. By the 2006 census, the State’s population is 3,950,249 comprising 2,032,725 males and 1,917,524 females.

Ethnic groups: The easily identifiable major ethnic groups are Nupes, Hausa, Gbagyi, Kadara, Koro, Bassa, Kamuku, Ingwai, Fangu, Kambari, Dukkawa, Fulani, Abewa, Bisan, Gungawa, Bauchi, Bariba, Urah, Boko, Bokobaro, Bauchnu, Achifawa, Dakarkari, Kakanda, Ganagana, and Dibo and numerous non native tribes.
Economic activities: The major economic activity is agriculture: farming, fishing, and cattle rearing.
The other economic activities (though limited in scale) include banking, trading, transportation, local arts and crafts with Bida, the heart land of the Nupes, famous for its brass work. These activities constitute the means of livelihood of the people of Niger State in addition to public service.
Reference: nigerstate.gov.ng/about-niger