The languages in Angola are Portuguese and those originally spoken by the different ethnic groups. Portuguese was introduced during the Portuguese colonial era. The most widely spoken indigenous languages are Umbundu, Kimbundu and Kikongo, in that order.
Portuguese is the official language of the country.
In 2014, a census carried out by the Instituto Nacional de Estatística in Angola states that 71.15% of the nearly 25.8 million inhabitants of Angola (meaning around 18.3 million people) use Portuguese as a first or second language.
Languages in Angola (2014 Census)
- Portuguese 71.1%
- Umbundu 23.0%
- Kikongo 8.2%
- Kimbundu 7.8%
- Chokwe 6.5%
- Nyaneka 3.4%
- Ngangela 3.1%
- Fiote 2.4%
- Kwanyama 2.3%
- Muhumbi 2.1%
- Luvale 1.0%
- Other 4.1%
| Language | Percent |
| Portuguese | 71.10% |
| Umbundu | 23.00% |
| Kikongo | 8.20% |
| Kimbundu | 7.80% |
| Chokwe | 6.50% |
| Nyaneka | 3.40% |
| Ngangela | 3.10% |
| Fiote | 2.40% |
| Kwanyama | 2.30% |
| Muhumbi | 2.10% |
| Luvale | 1.00% |
| Other | 4.10% |
The official and most widely spoken language in Angola is Portuguese. It is spoken by over 70% of the people of Angola. Portuguese language is followed by Umbundu with 23%. Umbundu happens to be the largest ethnic group in Angola.
The languages in Angola are Portuguese and those originally spoken by the different ethnic groups.
Portuguese was introduced during the Portuguese colonial era.
The most widely spoken indigenous languages are Umbundu, Kimbundu and Kikongo, in that order.
In 2014, a census carried out by the Instituto Nacional de Estatística in Angola states that 71.15% of the nearly 25.8 million inhabitants of Angola (meaning around 18.3 million people) use Portuguese as a first or second language.
Angola
Angola is a country on the west-central coast of Southern Africa. It is bordered by Namibia to the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Zambia to the east, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west.

Angola has an exclave province, the province of Cabinda, that borders the Republic of the Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
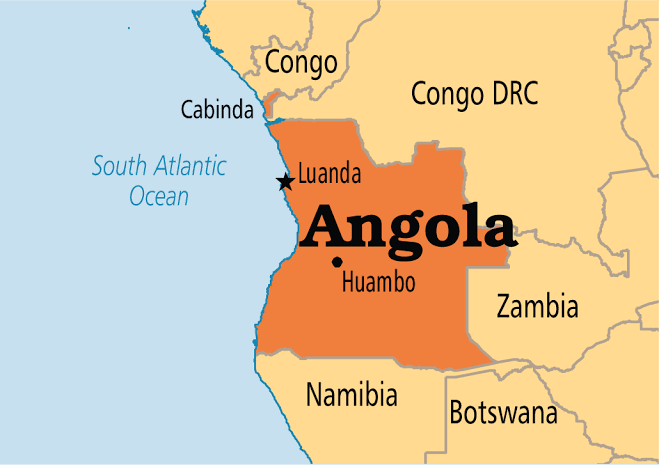

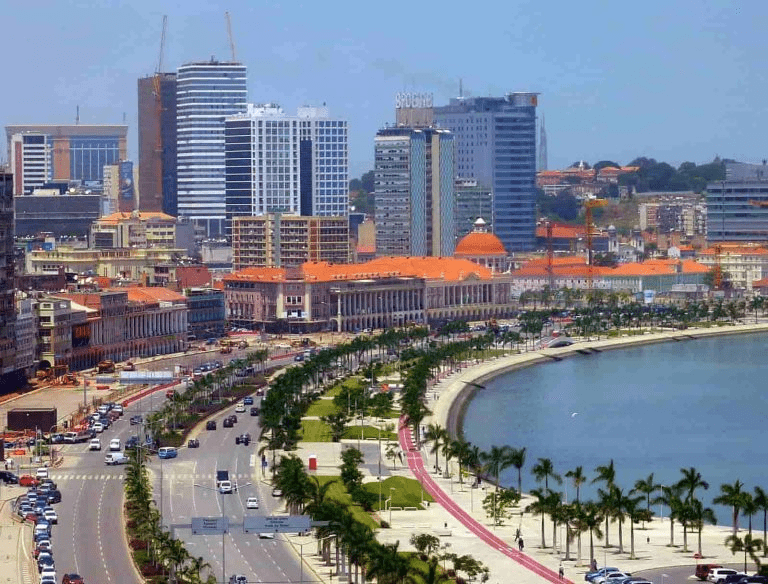
The capital and most populous city is Luanda.
Basic facts
Capital: Luanda
Official language: Portuguese
Currency: Angolan Kwanza
Government: Republic, Presidential system, Unitary state
Population: 34.5 million (2021) World Bank
Dialing code: +244
| Urban Population, 2020: | 66.8% |
| Female Population, 2020: | 51.2% |
| GDP: | US$ 58.5 Billion |
| GNI Per Capita 2016: | US$ 2,230 |
| Inflation Rate December 2020: | 25.1% |
| Crude Birth Rate 2020(per 1000): | 42.72% |
| Human Development Index (rank / 189): | 148 |
| Human Development Index (scale 0 to 1): | 0.581 |
| Membership Date: | 23/06/1980 |
| Cumulative Approvals (1980-2021): | UA 2.95 Billion |




As of 2021, the Angolan population is estimated at 32.87 million. Angola is multicultural and multiethnic. Angolan culture reflects centuries of Portuguese influence, namely the predominance of the Portuguese language and of the Catholic Church, intermingled with a variety of indigenous customs and traditions.
Angola has vast mineral and petroleum reserves, and its economy is among the fastest-growing in the world, especially since the end of the civil war; however, economic growth is highly uneven, with most of the nation’s wealth concentrated in a disproportionately small part of the population.
The standard of living remains low for most Angolans; life expectancy is among the lowest in the world, while infant mortality is among the highest.
The largest investment and trade partners are China, the European Union, and the United States.
Angola is a member of the United Nations, African Union, the Community of Portuguese Language Countries, and the Southern African Development Community.



