The density of Algeria population is 1 person per 14 km2.
The density according to the provinces is as follows:
| Province | Density per km2 |
|---|---|
| Adrar | 1.03 |
| Chlef | 209 |
| Laghouat | 18 |
| Oum El Bouaghi | 81 |
| Batna | 92 |
| Béjaïa | 279 |
| Biskra | 57 |
| Béchar | 3.61 |
| Blida | 591 |
| Bouïra | 157 |
| Tamanrasset | 0.34 |
| Tébessa | 46 |
| Tlemcen | 105 |
| Tiaret | 41 |
| Tizi Ouzou | 316 |
| Algiers | 2,511 |
| Djelfa | 46 |
| Jijel | 247 |
| Sétif | 229 |
| Saïda | 49 |
| Skikda | 223 |
| Sidi Bel Abbès | 66 |
| Annaba | 424 |
| Guelma | 118 |
| Constantine | 427 |
| Médéa | 92 |
| Mostaganem | 325 |
| M’Sila | 53 |
| Mascara | 132 |
| Ouargla | 1.6 |
| Oran | 688 |
| El Bayadh | 3.2 |
| Illizi | 0.17 |
| Bordj Bou Arréridj | 160 |
| Boumerdès | 504 |
| El Tarf | 122 |
| Tindouf | 0.31 |
| Tissemsilt | 93 |
| El Oued | 10.61 |
| Khenchela | 40 |
| Souk Ahras | 95 |
| Tipaza | 273 |
| Mila | 220 |
| Aïn Defla | 156 |
| Naâma | 6.5 |
| Aïn Témouchent | 156 |
| Ghardaïa | 12.82 |
| Relizane | 152 |
| Timimoun | 1.9 |
| Bordj Badji Mokhtar | 0.14 |
| Ouled Djellal | 15 |
| Béni Abbès | 0.49 |
| Ain Salah | 0.38 |
| Ain Guezzam | 0.13 |
| Touggourt | 14 |
| Djanet | 0.2 |
| El M’Ghair | 0.94 |
| El Menia | 0.92 |
| Total | 14 |
The total population of Algeria (2008) is 34,080,030.
Population of Algeria by province is as follows:
| Province | Population |
|---|---|
| Adrar | 261,258 |
| Chlef | 1,002,088 |
| Laghouat | 455,602 |
| Oum El Bouaghi | 621,612 |
| Batna | 1,119,791 |
| Béjaïa | 912,577 |
| Biskra | 547,137 |
| Béchar | 219,898 |
| Blida | 1,002,937 |
| Bouïra | 695,583 |
| Tamanrasset | 115,043 |
| Tébessa | 648,703 |
| Tlemcen | 949,135 |
| Tiaret | 846,823 |
| Tizi Ouzou | 1,127,608 |
| Algiers | 2,988,145 |
| Djelfa | 1,092,184 |
| Jijel | 636,948 |
| Sétif | 1,489,979 |
| Saïda | 330,641 |
| Skikda | 898,680 |
| Sidi Bel Abbès | 604,744 |
| Annaba | 609,499 |
| Guelma | 482,430 |
| Constantine | 938,475 |
| Médéa | 819,932 |
| Mostaganem | 737,118 |
| M’Sila | 990,591 |
| Mascara | 784,073 |
| Ouargla | 311,337 |
| Oran | 1,584,607 |
| El Bayadh | 228,624 |
| Illizi | 34,715 |
| Bordj Bou Arréridj | 628,475 |
| Boumerdès | 802,083 |
| El Tarf | 408,414 |
| Tindouf | 49,149 |
| Tissemsilt | 294,476 |
| El Oued | 647,548 |
| Khenchela | 386,683 |
| Souk Ahras | 438,127 |
| Tipaza | 591,010 |
| Mila | 766,886 |
| Aïn Defla | 766,013 |
| Naâma | 192,891 |
| Aïn Témouchent | 371,239 |
| Ghardaïa | 306,322 |
| Relizane | 726,180 |
| Timimoun | 122,019 |
| Bordj Badji Mokhtar | 16,437 |
| Ouled Djellal | 174,219 |
| Béni Abbès | 50,163 |
| Ain Salah | 50,392 |
| Ain Guezzam | 11,202 |
| Touggourt | 247,221 |
| Djanet | 17,618 |
| El M’Ghair | 162,267 |
| El Menia | 57,276 |
| Country total | 34,080,030 |
List of 58 provinces of Tunisia
The 58 provinces (wilayas) of Tunisia are:
- Adrar
- Aïn Defla
- Ain Guezzam
- Ain Salah
- Aïn Témouchent
- Algiers
- Annaba
- Batna
- Béchar
- Béjaïa
- Béni Abbès
- Biskra
- Blida
- Bordj Badji Mokhtar
- Bordj Bou Arréridj
- Bouïra
- Boumerdès
- Chlef
- Constantine
- Djanet
- Djelfa
- El Bayadh
- El Menia
- El M’Ghair
- El Oued
- El Tarf
- Ghardaïa
- Guelma
- Illizi
- Jijel
- Khenchela
- Laghouat
- Mascara
- Médéa
- Mila
- Mostaganem
- M’Sila
- Naâma
- Oran
- Ouargla
- Ouled Djellal
- Oum El Bouaghi
- Relizane
- Saïda
- Sétif
- Sidi Bel Abbès
- Skikda
- Souk Ahras
- Tamanrasset
- Tébessa
- Tiaret
- Timimoun
- Tindouf
- Tipaza
- Tissemsilt
- Tizi Ouzou
- Tlemcen
- Touggourt
More on the provinces of Tunisia
Algeria is divided into 58 provinces (wilayas), since December 18, 2019.
By 1984 the number of Algerian provinces was 48.
In 2019, 10 new provinces were added making te current total of 58..
The 58 provinces are divided into 1,541 municipalities (baladiyahs).
In the provinces are districts and municipalities.
- Provinces (wilayas)
- Districts (dairas)
- Municipalities
The name of a province is always that of its capital city.
A wilaya is a territorial collectivity enjoying economic and diplomatic freedom.
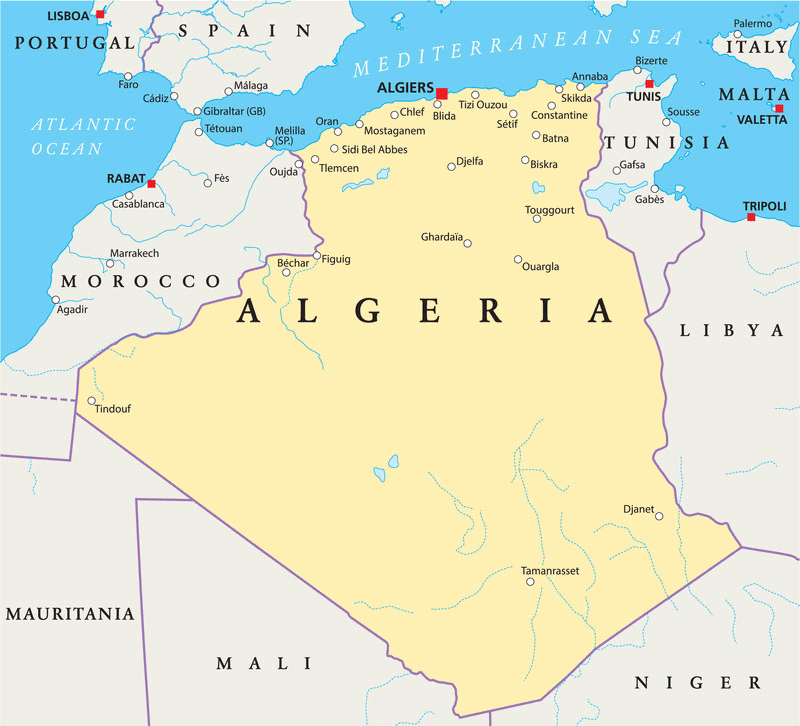
Algeria
Algeria is country in North Africa. It is the largest country on the continent and the tenth-largest in the world by area, covering more than 2.3 million square kilometers.
Capital: Algiers (El Djazaïr)
Official languages: Arabic, Tamazight
Government: Semi-presidential system
Currency: Algerian Dinar
Area: 2,382,000 sq km
Total Population (2017): 41.1 Million
Urban Population (2017): 73.50%
Female Population (2017): 49.70%




It has a coastline of about 1,200 kilometers along the Mediterranean Sea, and shares borders with Tunisia, Libya, Niger, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, and Western Sahara.
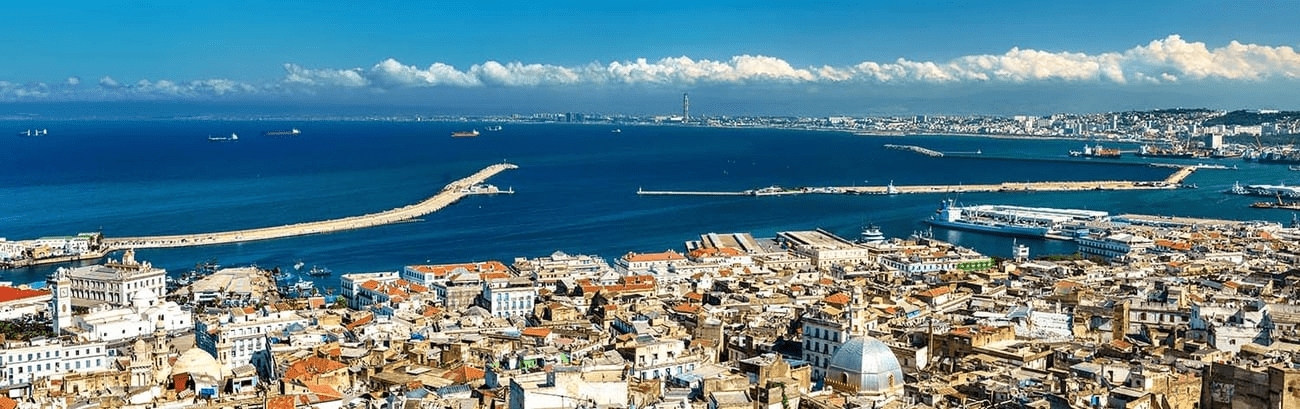

It has a Mediterranean coastline of over 1200 km and a contrasting relief made up of plains, high plateaus, mountain ranges and a desert expanse of 2 million km² which is rich in natural and historical elements that represent the preserved memory of the southern Algerian region.
Algeria has:
- 1557 hotel establishments with a capacity of 143811 beds, including about 20000 beds, are in the public sector (HTT Group), which are currently being rehabilitated and modernised,
- 609 beaches listed, of which 427 are authorised for swimming,
- 10 national parks including Tassili National Park (100,000 ha) and Ahaggar National Park (Hoggar 000 ha), wetlands, 51 of which are classified by the Ramsar Convention, as well as a rich thermal potential.
- 7 Algerian monuments and sites are listed as World Heritage Sites: Tassili n’Ajjer, in the wilayas of Tamanrasset and Illizi, Djamila in the wilaya of Setif, the M’Zab valley in the wilaya of Ghardaïa, the Kasbah of Algiers, the Kalaa of Beni Hamad in the wilaya of M’sila, Timgad in the wilaya of Batna, Gourraya in the wilaya of Tipaza.
- 36 airports, including 16 international airports.
- 80 dams and 20 seawater treatment plants, in addition to 15 large power plants.
- A road network of nearly 127,000 kms.
- Railway tracks reaching 6300 km, in addition to the metro and tramway network at the level of 07 wilayas.
- A telecommunications network covering most of the country.
Algeria gained its independence in 1962 after a war of liberation that lasted eight years.
The country has a rich and diverse history, culture, and geography, with influences from various civilizations such as Berbers, Phoenicians, Romans, Arabs, Turks, and French.
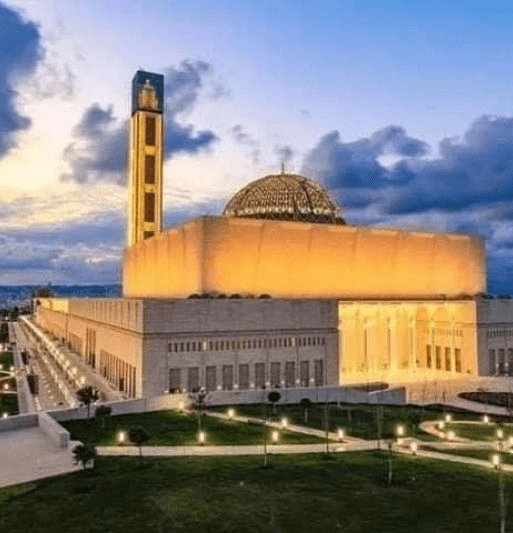


The country was part of the Ottoman Empire until the early 19th century, when it was colonized by France.
Algeria is a member of the African Union, the Arab League, OPEC, and the United Nations, and has diplomatic relations with many countries around the world. It plays an important role in regional and international affairs, especially in Africa and the Middle East. Algeria is also a founding member of the Arab Maghreb Union, a regional organization that aims to promote cooperation and integration among its members.
The country has a population of about 44 million people, most of whom are Arab-Berbers or Amazighs, who speak Arabic and Tamazight as official languages. Algeria is a multiethnic and multicultural society, with other ethnic groups such as Tuaregs, Sahrawis, Mozabites, Chaouis, and Kabyles. Algeria also has a religious diversity, with Islam being the state religion and the majority faith, but also having minorities of Christians, Jews, and other beliefs.
It has a mixed economy, with a large public sector and a growing private sector. The main sectors are hydrocarbons, agriculture, industry, services, and tourism. Hydrocarbons account for about 60% of the government revenues and 30% of the GDP. It is one of the largest producers and exporters of natural gas and oil in the world. Agriculture employs about 14% of the workforce and contributes to 12% of the GDP. The main crops are wheat, barley, potatoes, dates, olives, citrus fruits, grapes, and almonds. Industry accounts for 37% of the GDP and includes sectors such as petrochemicals, metallurgy, textiles, food processing, electronics, and construction. Services make up 51% of the GDP and include sectors such as banking, telecommunications, transportation, education, health care, and retail. Tourism is a potential source of income and employment for Algeria, with its natural and cultural attractions such as the Sahara desert, the Atlas mountains, the Roman ruins of Timgad and Djemila, the Casbah of Algiers, and the M’Zab Valley.
Algeria faces many challenges and opportunities in the 21st century, such as political and social reforms, economic diversification, environmental protection,regional stability and international cooperation. It has experienced political unrest and social protests in recent years, demanding more democracy, accountability and transparency from the government.
It seeks to diversify its economy and reduce its dependence on hydrocarbons which are vulnerable to price fluctuations and depletion. The country has moves deal with environmental issues such as desertification, water scarcity, pollution, and climate change which threaten its natural resources and human well-being. Also it seeks to maintain its security and stability in a volatile region, facing threats from terrorism, extremism and armed conflicts in neighboring countries. Algeria is determined to enhance its cooperation and integration with other countries and regional organizations to foster trade, investment, development and peace.
Reference: aapi.dz/