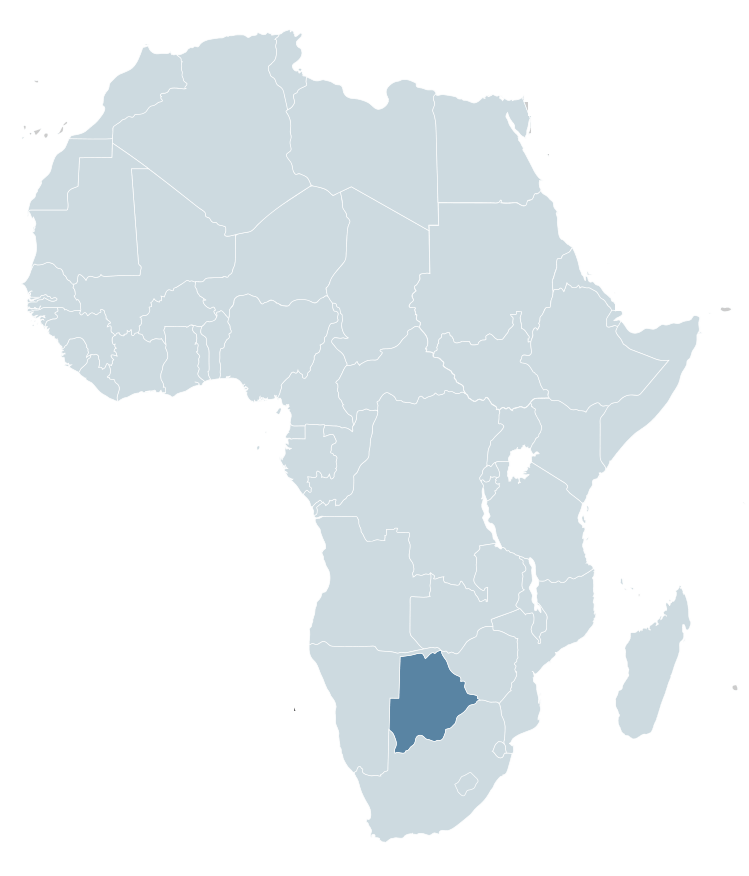
Botswana is best known for its diamonds mining, variety of wildlife, a large desert and an inland delta.
Although diamond mining accounts for about 94 percent of Botswana’s income, the country also has significant copper, nickel, cobalt, gold. soda ash. and coal deposits which are currently being explored and developed.
Most diamonds are mined from subterranean geological structures called volcanic pipes.
Volcanic pipes form when volcanoes erupt deep within the earth.
Pipes are composed mainly of two rock types, kimberlite and lamproite.
The intense pressure and high temperatures found in the pipes help to form the diamonds.
Kimberlite was named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa. the the discovery of a gigantic diamond created a diamond rush in 1871,
The boom in Botswana’s mining industry began in the late 1960s when
the South African company De Beers discovered quantities of garnet and
other stones indicative of the presence of diamonds in Botswana.
In 1967, the largest diamond pipe in the world was discovered at Orapa,
northeast of the Central Kalahari Game Reserve.
Debswana Diamond Company
De Beers quickly entered into a partnership with the government of Botswana to form the Debswana Diamond Company Ltd.
Debswana owns four major diamond mines in Botswana.
The first mine began production at Orapa in 1972, followed
by Letlhakane in 1975, then Jwaneng in 1982. and Damtshaa in 2003.
In December 2004, Debswana negotiated 25-year lease renewals for all four of its mines with the government of Botswana.
However, in November 2020, it announced that it would close its Damtshaa mine from 2021 to 2024. as the COVID-19 had lowered demand for the lower-quality diamonds found in that mine.
Botswana is the largest producer of gem diamonds – diamonds that are
used in fine jewelry – in the world, but it also produces industrial diamonds which are used in many manufacturing processes.
Because they are the hardest substance on earth. diamonds can be used to prevent machine parts from rubbing against each other and wearing down.
More on Botswana
Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahari Desert.
It is bordered by South Africa to the south and southeast, Namibia to the west and north, and Zimbabwe to the northeast.
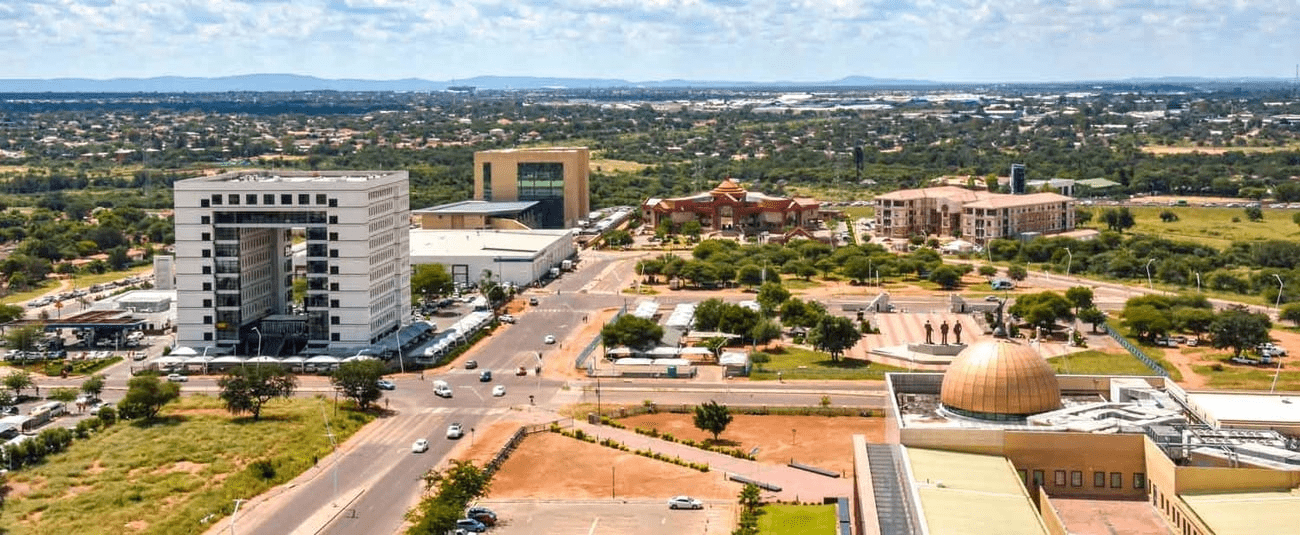
Capital: Gaborone
Currency: Botswanan Pula
Official language: English
Population: 2.588 million (2021) World Bank
Dialing code: +267
Gross Domestic Product: 17.61 billion USD (2021) World Bank
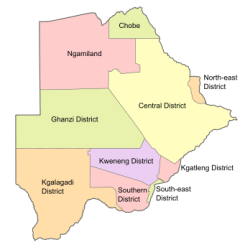
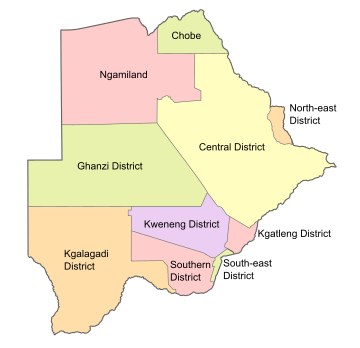
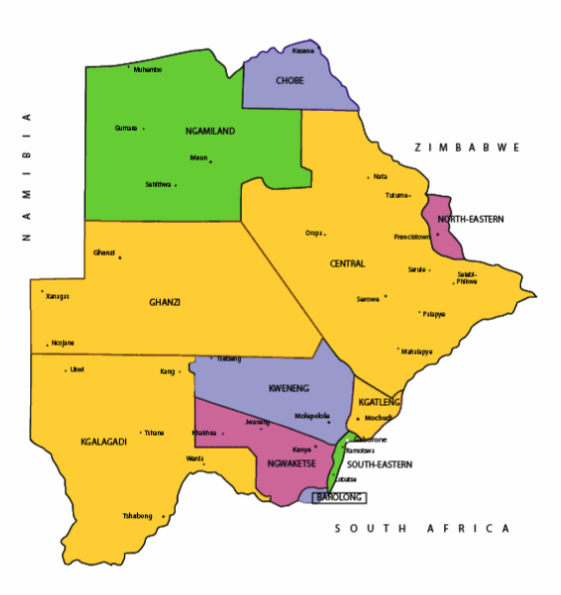
Botswana’s ten districts are:
- Southern District
- South-East District
- Kweneng District
- Kgatleng District
- Central District
- North-East District
- Ngamiland District
- Kgalagadi District
- Chobe District
- Ghanzi District
Botswana’s councils created from urban or town councils are: Gaborone City, Francistown, Lobatse Town, Selebi-Phikwe Town, Jwaneng Town, Orapa Town and Sowa Township.

The name Botswana refers to ‘Land of the Tswana’. The landlocked, Southern Africa country is officially known as the Republic of Botswana.













Botswana is connected to Zambia through the Kazungula Bridge making it the world’s shortest border between two countries.
A country of slightly over 2 million people (2021), Botswana is one of the most sparsely populated countries in the world. It is essentially the nation state of the Tswana ethnic group, who make up 79% of the population.

About 11.6 per cent of the population lives in the capital and largest city, Gaborone.
Formerly one of the world’s poorest countries—with a GDP per capita of about US$70 per year in the late 1960s—it has since transformed itself into an upper-middle-income country, with one of the world’s fastest-growing economies.


The Tswana ethnic group were descended mainly from Bantu-speaking tribes who migrated southward of Africa to modern Botswana, living in tribal enclaves as farmers and herders.



In 1885, the British colonised the area and declared a protectorate under the name of Bechuanaland.
As colonisation stopped, Bechuanaland became an independent republic under its current name on 30 September 1966.


Since then, it has been a representative republic, with a consistent record of uninterrupted democratic elections and the lowest perceived corruption ranking in Africa since at least 1998.

The economy is dominated by mining and tourism. Botswana has a GDP (purchasing power parity) per capita of about $18,113 as of 2021, one of the highest in subsaharan Africa.


Botswana is the world’s biggest diamond producing country.
Its relatively high gross national income per capita gives the country a high standard of living and the third-highest Human Development Index of continental Sub-Saharan Africa (after Gabon and South Africa).
The country has been adversely affected by the HIV/AIDS epidemic. In 2002, Botswana began offering anti-retroviral drugs (ARVs) to help combat the epidemic.
Botswana is a member of the Southern African Customs Union, the Southern African Development Community, the Commonwealth of Nations, and the United Nations.