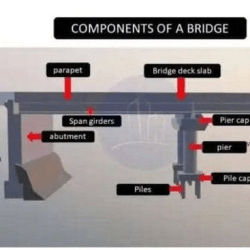
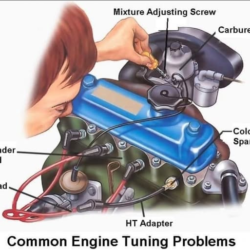
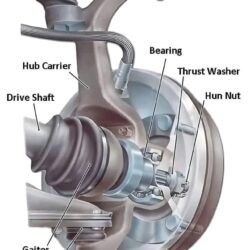
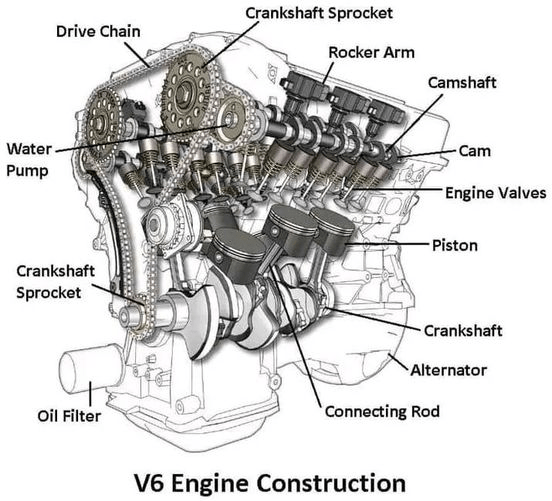
The internal combustion engine is a marvel of engineering, transforming fuel into motion through a precisely timed series of mechanical and chemical events. At its core, the engine depends on various interconnected components working harmoniously. Below, we explore the key components of a car engine, their roles, and how they contribute to the engine’s overall functionality.
Understanding the key components of a car engine reveals the intricate synergy required for its operation. From the rocker arm to the piston, each part has a unique and vital function. This harmonious interplay of components is what makes the internal combustion engine a remarkable achievement in automotive engineering.
1. Rocker Arm
- Function: The rocker arm plays a pivotal role in controlling the intake and exhaust valves. It acts as a lever, transferring motion from the camshaft to the valves.
- How it Works: The camshaft lobes push the rocker arm, which in turn opens or closes the valves at the appropriate times.
- Importance: Proper valve timing ensures the efficient entry of the air-fuel mixture and exit of exhaust gases, critical for optimal engine performance.
2. Cylinder Head
- Function: The cylinder head forms the upper boundary of the combustion chamber, where fuel is burned to produce energy.
- Additional Features:
- It contains ports for air and fuel intake, as well as exhaust outlets.
- It houses components such as the spark plug and valves.
- Importance: The cylinder head also helps dissipate heat generated during combustion, ensuring the engine does not overheat.
3. Cylinder Block
- Function: Often referred to as the “heart of the engine,” the cylinder block is the engine’s foundation, housing the cylinders where combustion occurs.
- Design: It is made of strong materials like cast iron or aluminum alloy to withstand high pressure and temperature.
- Importance: Besides housing the cylinders, the block also contains passageways for coolant and oil, crucial for engine lubrication and temperature regulation.
4. Engine Valves
- Function: Engine valves regulate the flow of air and fuel into the combustion chamber and allow exhaust gases to exit.
- Intake Valves: Allow the air-fuel mixture to enter.
- Exhaust Valves: Let burnt gases escape.
- Operation: Controlled by the camshaft, they open and close in sync with the engine’s cycle.
- Importance: Precise valve timing is essential for efficient engine operation and performance.
5. Spark Plug
- Function: The spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture in the cylinder, triggering combustion.
- How it Works: It generates a high-voltage spark at the right moment, initiating the explosion that drives the piston downward.
- Importance: A properly functioning spark plug ensures smooth engine starts and optimal fuel efficiency.
6. Camshaft
- Function: The camshaft controls the opening and closing of valves, coordinating them with the piston’s movement.
- Design: It features lobes (cams) that press against the rocker arms to operate the valves.
- Importance: The timing of the camshaft is critical for maintaining the correct air-fuel mixture and exhaust cycle.
7. Crankshaft
- Function: The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which ultimately powers the vehicle’s wheels.
- How it Works: Connected to the pistons via connecting rods, it spins continuously as the engine cycles.
- Importance: The crankshaft is central to transferring engine power to the drivetrain.
8. Flywheel
- Function: The flywheel helps regulate and smooth out the engine’s power output by storing energy.
- How it Works: It absorbs kinetic energy during the power stroke and releases it during non-power strokes, ensuring steady engine operation.
- Importance: It reduces vibrations and helps maintain consistent engine speed.
9. Connecting Rod
- Function: The connecting rod links the piston to the crankshaft, transmitting the force generated by combustion.
- Design: It is typically made of lightweight yet durable materials to handle high stress.
- Importance: It converts the piston’s reciprocating motion into rotary motion via the crankshaft.
10. Piston
- Function: The piston compresses the air-fuel mixture and transforms the energy from combustion into mechanical motion.
- How it Works:
- During the compression stroke, the piston rises to compress the mixture.
- During the power stroke, the explosion pushes the piston downward, creating force.
- Importance: The piston is integral to generating the power that propels the vehicle.
How These Components Work Together
The car engine operates through a four-stroke cycle:
- Intake: The intake valve opens, and the piston moves downward, drawing in the air-fuel mixture.
- Compression: The piston rises, compressing the mixture for efficient combustion.
- Power: The spark plug ignites the mixture, and the explosion pushes the piston downward.
- Exhaust: The exhaust valve opens, allowing burnt gases to exit as the piston rises again.
Each component plays a role in this cycle, ensuring the engine runs efficiently and reliably.