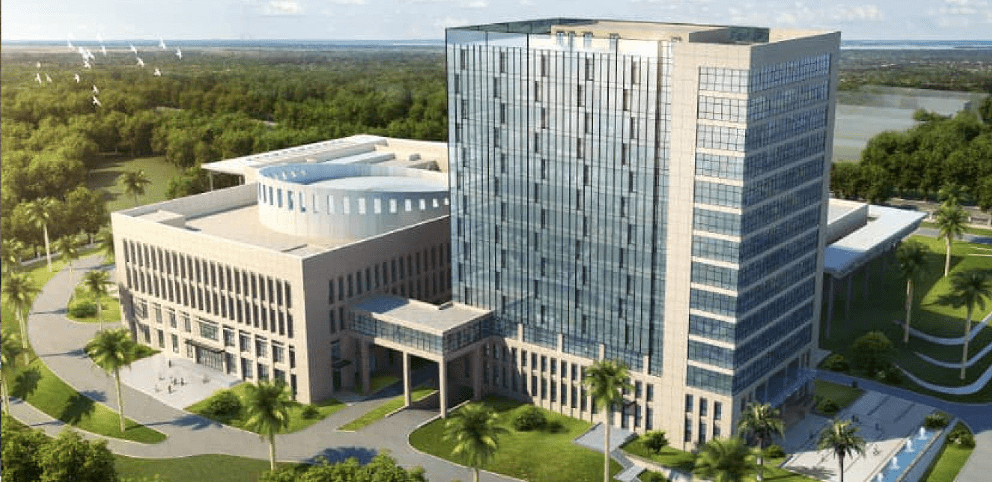
The National Assembly of Cameroon legislates and oversees government activities.

Address
Yaounde, Cameroon
Tel : +237 222 22 04 84
Sittings at the National Assembly
Sittings of the National Assembly shall be made public. The National Assembly may exceptionally hold sittings in camera at the request of the President of the Republic or of an absolute majority of its members.
Plenary sittings:
At the beginning of the legislative period and the first ordinary session of the year, the National Assembly holds plenary sittings essentially devoted to the installation of the Provisional Bureau, the validation of mandates and the election of its Bureau.
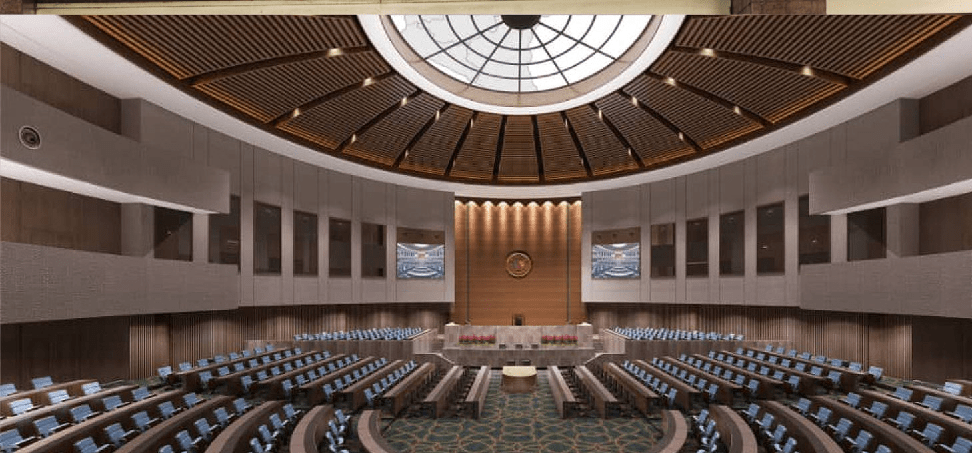

A plenary sitting is held when the Chairmen’s Conference so decides and for a specific agenda.
The agendas of plenary sittings are determined by the Chairmen’s Conference.
Sessions
- Statutory session: At the beginning of the legislative period, the National Assembly shall meet in a statutory ordinary session on the second Tuesday following the proclamation of the parliamentary election results by the Constitutional Council.
- Ordinary sessions: Each year, the National Assembly shall hold 3 (three) ordinary sessions, each lasting not more than 30 (thirty) days, in March, June and November.
- Extraordinary sessions: The National Assembly may, in accordance with the Constitution, meet in extraordinary session for not more than 15 (fifteen) days on a specific agenda at the request of the President of the Republic or of one third of its members.
The extraordinary session shall wind up as soon as the agenda for which it was convened is exhausted.
Legislative Procedure
- Admissibility of bills
- Announcement of bills in plenary
- Committee proceedings
- Committee reports
- Plenary sitting for adoption
- Parliamentary shuttling
- Signing and forwarding of bills
- Enactment by the President of the Republic
Organization
The National Assembly is composed of one hundred and eighty (180) deputies elected by universal, direct and secret suffrage for a five-year term. It is made up of the following Organs:
I – The Governing Bodies
1- The Office
The National Assembly has a Bureau elected at the beginning of each legislative year. This Office is made up of:
- A President
- A First Vice-President
- Five Vice-Presidents
- Four Quaestors
- Twelve Secretaries
This office is assisted by a Secretary General, an ex officio member, Legal and Parliamentary Advisor of the National Assembly.
2- The Conference of Presidents
Pursuant to the provisions of Article 27 of Law No. 73/1 of 08 June 1973 on the Rules of Procedure of the National Assembly, the Conference of Presidents is a collegiate body comprising:
- The President of the National Assembly
- Members of the Bureau of the National Assembly
- The members of each of the nine general commissions
- The Presidents of the Groups.
A member of the Government participates in the work of this conference. The main role of the Conference of Presidents is to:
- Setting the agenda for the work of the National Assembly
- Decide on the admissibility of bills and proposals submitted to the National Assembly
- Entrust these texts to the competent committees
- Setting the date for the various plenary sessions
II- Inner Formations
The internal formations of the National Assembly are the Groups and the General Committees, the ad hoc committees, the special committees and the commissions of inquiry.













