Gombe State in northeastern Nigeria has vibrant traditional leadership, which includes Emirates, Chiefdoms, and Senior District Heads. These traditional institutions are integral to the cultural, social, and even political fabric of the region. They help maintain peace, facilitate community development, and preserve customs and traditions that date back centuries. This article explores the roles, histories, and contributions of these leaders across Gombe’s Emirates, Chiefdoms, and Senior Districts.
Understanding Gombe’s Traditional Leadership Structure
Gombe’s traditional leadership system has roots that stretch deep into its past, showcasing a complex blend of Emirates, Chiefdoms, and Senior District Heads. Each has distinct roles and responsibilities that cater to the unique ethnic and cultural composition of the state. Together, they form a network that promotes stability, cultural preservation, and local governance.
Gombe Emirates
Gombe is home to several prominent Emirates, each led by an Emir who serves as both a spiritual and community leader. The following are the major Emirates in Gombe:
1. Emir of Deba
The Emirate of Deba is known for its rich history and cultural contributions to the state. The Emir of Deba plays a critical role in promoting local traditions, encouraging community solidarity, and supporting local governance initiatives. The Emir’s influence extends into areas like conflict resolution, traditional celebrations, and local economic development.
2. Emir of Dukku
Dukku, one of the most influential Emirates, has a storied history and holds significant importance for the people of Gombe. The Emir of Dukku is respected for upholding the area’s customs and traditions, and his guidance is sought in both personal and communal matters. Community gatherings and events in Dukku are often presided over by the Emir, who also engages with local leaders to address challenges facing the populace.
3. Emir of Funakaye
The Emir of Funakaye, another notable Emirate, has a long-standing legacy of promoting cultural and social cohesion. Known for its vibrant festivals and traditional celebrations, Funakaye Emirate is pivotal in preserving the heritage of the people. The Emir also works closely with other traditional leaders to maintain peace and security.
4. Emir of Gombe
The Gombe Emirate is central to the traditional leadership in the state. As one of the oldest Emirates, the Emir of Gombe holds a revered position and is deeply involved in the state’s socio-political matters. The Emirate is often the primary point of reference for traditional rulership and is instrumental in major state events, representing a blend of historical reverence and modern governance.
5. Emir of Gona
The Gona Emirate, while smaller in comparison to others, plays an important role in maintaining cultural identity within its communities. The Emir of Gona oversees cultural preservation efforts, mediates disputes, and engages in projects aimed at improving the welfare of his people.
6. Emir of Nafada
Nafada, located in the northern part of Gombe State, has a rich history associated with its Emirate. The Emir of Nafada is dedicated to promoting the region’s customs and is often involved in religious and cultural activities that highlight the traditional values of the people.
7. Emir of Pindiga
Pindiga Emirate is well-known for its contributions to the cultural landscape of Gombe. The Emir of Pindiga frequently engages in activities that foster unity and cohesion among residents. The Emirate also plays a role in encouraging youth participation in traditional activities, helping to bridge the generational gap.
8. Emir of Yamaltu
Yamaltu Emirate is significant for its role in community development and cultural heritage. The Emir of Yamaltu works with local organizations to empower youths, support local businesses, and promote education within his jurisdiction. Traditional festivals celebrated here are widely attended and are an opportunity to unite the community.
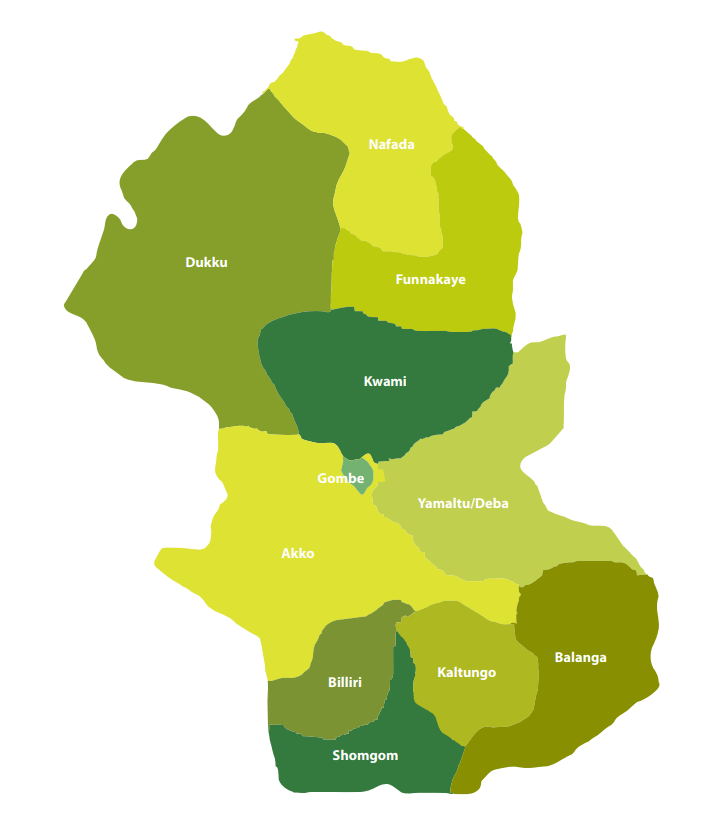

Chiefdoms in Gombe State
Chiefdoms in Gombe are traditionally smaller than Emirates but are equally important in preserving the cultural fabric of their communities. Each Chiefdom is led by a Chief, who has authority over specific ethnic groups or regions.
1. Balanga Chiefdom
The Balanga Chiefdom is known for its ethnic diversity, and the Chief of Balanga plays an essential role in promoting unity among the people. With a focus on cultural activities and traditional education, the Chiefdom is active in preserving heritage and promoting local customs.
2. Mai Tangale (Billiri)
The Mai Tangale of Billiri is a notable figure among the Tangale people. This Chiefdom is respected for its rich history, with the Mai Tangale serving as a unifying figure who promotes peace and stability. The Chiefdom is also known for its vibrant festivals and traditional ceremonies that attract visitors from across Nigeria.
3. Folo Dadiya
The Folo Dadiya Chiefdom, home to the Dadiya people, holds cultural preservation in high regard. The Chief, or Folo, of Dadiya oversees the promotion of Dadiya language, traditions, and customs, ensuring they remain a vital part of the community’s identity.
4. Mai Kaltungo
The Mai of Kaltungo is a well-regarded figure in Gombe, known for his commitment to social welfare and educational initiatives. Under his leadership, the Kaltungo Chiefdom has undertaken several initiatives to promote literacy and vocational training, supporting youth and contributing to local economic development.
5. Mai Tula
The Mai of Tula, another esteemed leader, promotes the cultural heritage of his people and often collaborates with local authorities to address community needs. The Tula Chiefdom is known for its dedication to preserving history and hosting cultural events that showcase its rich traditions.
6. Dala Waja
The Dala Waja Chiefdom is recognized for its dedication to maintaining social order and traditional governance. The leader of this Chiefdom plays a significant role in community decisions, working closely with local organizations to enhance the quality of life for residents.
Senior District Heads
Senior District Heads in Gombe are key figures within the traditional hierarchy, tasked with governing specific districts. They collaborate closely with Emirs and Chiefs, often serving as intermediaries between the traditional leaders and the government.
1. District Head of Gombe
The District Head of Gombe is a significant authority in the region, responsible for overseeing local matters and ensuring that the directives from the Emir are implemented. The role involves conflict mediation, community development initiatives, and supporting local governance structures.
2. District Head of Kwami
In Kwami, the District Head is crucial to community welfare, often organizing local events and addressing issues related to rural development. The District Head of Kwami works to promote unity and ensure that the values and traditions of the community are respected and upheld.
The Role of Traditional Leaders in Modern Gombe
The leaders of Gombe’s Emirates, Chiefdoms, and Districts play a vital role in bridging tradition with modernity. They often partner with the government on issues such as health, education, and youth empowerment. Emirs and Chiefs frequently advocate for peace, support educational initiatives, and promote environmental conservation. Their roles extend beyond ceremonial duties, as they actively engage with both the state government and NGOs to foster community development.