Bi’r Hima, located in southwestern Saudi Arabia, is indeed one of the most significant archaeological sites in the world, offering a fascinating window into the ancient history of the Arabian Peninsula.
Location: Situated in the Najran Province of southwestern Saudi Arabia, Bi’r Hima lies along ancient trade routes that connected the Arabian Peninsula to the Mediterranean and beyond.
Significance: The site is renowned for its rock art and inscriptions, which date back as far as 7,000 years, making it one of the oldest and richest collections of prehistoric art in the world.
UNESCO World Heritage Site: Bi’r Hima was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2021, recognizing its outstanding cultural and historical value.
Rock Art and Inscriptions
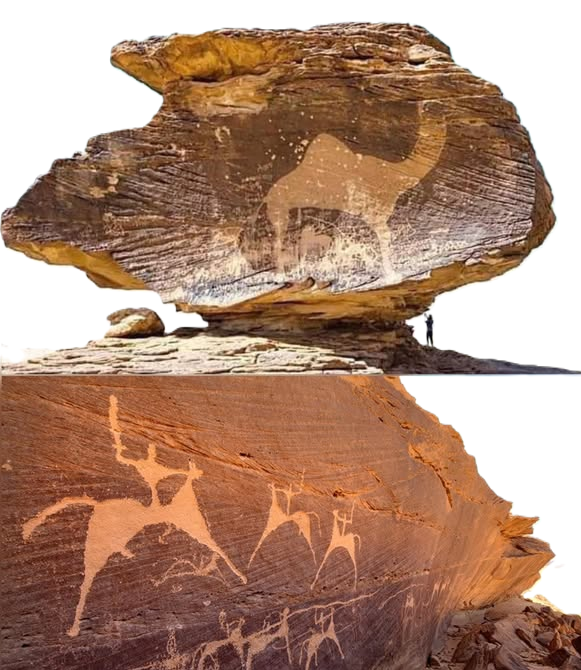
Petroglyphs: The site features thousands of petroglyphs (rock carvings) that depict a wide range of subjects, including:
Animals: Camels, ostriches, ibexes, and even extinct species like lions, suggesting a more fertile environment in ancient times.
Human Figures: Scenes of hunting, dancing, and daily life, providing insights into the social and cultural practices of ancient communities.
Symbols and Scripts: Early forms of writing, such as Musnad (an ancient South Arabian script) and Aramaic-Nabatean, reflect the cultural crossroads of the region.
Themes: The carvings often depict hunting scenes, rituals, and mythological symbols, offering clues about the beliefs and survival strategies of ancient peoples.
Historical and Cultural Context
Ancient Trade Routes: Bi’r Hima was a critical stop along the incense trade routes, which transported precious goods like frankincense and myrrh from southern Arabia to the Mediterranean. The site served as a meeting point for traders, travelers, and tribes.
Cultural Exchange: The inscriptions and carvings reveal a blend of influences from South Arabian, Nabatean, and early Arabic cultures, highlighting the region’s role as a cultural melting pot.
Tribal Agreements: Some carvings are believed to commemorate tribal agreements or rituals, serving as early records of social and political life in ancient Arabia.
Archaeological Discoveries
Dating: The rock art at Bi’r Hima spans thousands of years, with some carvings dating back to the Neolithic period (around 5,000 BCE) and others from later periods, such as the Bronze Age and Iron Age.
Environmental Clues: The depictions of animals like lions and ibexes suggest that the region was once more fertile and supported a diverse range of wildlife.
Human History: The site provides valuable insights into the daily lives, beliefs, and survival strategies of ancient Arabian communities, including their adaptation to a changing environment.
UNESCO Recognition
Criteria for Inscription: Bi’r Hima was recognized by UNESCO for its outstanding universal value, particularly its role as a cultural crossroads and its rich collection of rock art.
Preservation Efforts: The Saudi government and international organizations are working to preserve and protect the site, ensuring that its historical and cultural significance is maintained for future generations.
Visiting Bi’r Hima
Accessibility: While the site is remote, it is accessible to visitors interested in exploring its ancient wonders. Guided tours are available to help visitors understand the historical and cultural context of the rock art.
Best Time to Visit: The cooler months (October to March) are ideal for visiting, as the desert climate can be extremely hot during the summer.
Nearby Attractions: The Najran Province is also home to other historical sites, such as the Al-Ukhdood archaeological site and the Najran Fort, making it a fascinating destination for history enthusiasts.
Why Bi’r Hima Matters
Cultural Heritage: The site is a testament to the rich cultural heritage of the Arabian Peninsula, showcasing the creativity and resilience of ancient communities.

Historical Insights: The rock art and inscriptions provide valuable insights into the daily lives, beliefs, and trade networks of ancient peoples.
Environmental History: The depictions of extinct animals and changing landscapes offer clues about the region’s environmental history and the impact of climate change over millennia.
Global Significance: As a UNESCO World Heritage Site, Bi’r Hima is recognized as a site of global importance, contributing to our understanding of human history and cultural evolution.