These nine states form the backbone of Nigeria’s oil and gas industry, which supplies a majority of the country’s revenue. However, the region also faces significant socio-economic and environmental challenges:
- Environmental Degradation: Oil spills, gas flaring, and chemical pollution impact agriculture, fisheries, and health.
- Economic Inequality: Despite the wealth generated from oil, many communities in the Niger Delta remain impoverished.
- Social Unrest and Conflict: Tensions over resource control and environmental neglect have fueled unrest and calls for reform.
Efforts are ongoing to address these issues through various government initiatives, such as the Niger Delta Development Commission (NDDC) and the Ministry of Niger Delta Affairs, but achieving equitable and sustainable development in the region remains a complex challenge.
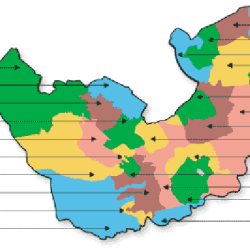
The Niger Delta region of Nigeria is a significant area known for its rich oil and gas reserves, which have a major impact on the Nigerian economy. This region encompasses nine states, covering both the South-South geopolitical zone and parts of the South-East and South-West zones. The Niger Delta is also known for its diverse ethnic communities and its complex socio-economic and environmental challenges.
The Nine States of the Niger Delta Region
- Abia State
- Akwa Ibom State
- Bayelsa State
- Cross River State
- Delta State
- Edo State
- Imo State
- Ondo State
- Rivers State
These states are home to approximately 1,500 communities and numerous oil and gas companies, making the Niger Delta the heart of Nigeria’s oil industry. This industry provides a large portion of Nigeria’s revenue but has also led to environmental degradation, pollution, and socio-economic challenges in the region.

Importance and Challenges of the Niger Delta Region
The Niger Delta region produces the vast majority of Nigeria’s crude oil, but the wealth generated from this resource has not been evenly distributed among the people. The region has faced:
- Environmental Degradation: Oil spills, gas flaring, and industrial waste have significantly damaged the ecosystem, affecting agriculture, fishing, and health.
- Economic Disparities: Despite the oil wealth, the local communities often face poverty, unemployment, and limited access to basic services.
- Social and Political Unrest: Frustrations over resource control, environmental neglect, and economic inequality have led to unrest, with various groups demanding a fairer share of the oil wealth.
The Niger Delta’s unique position as both an economic powerhouse and an area facing substantial socio-environmental issues makes it a focal point for both Nigerian policymakers and international observers.
The Niger Delta region in Nigeria, known for its abundant oil and gas resources, is composed of nine states. These states are located across the southern part of Nigeria and represent a mix of cultural, ethnic, and linguistic diversity. Here is an overview of each of the nine Niger Delta states:
1. Abia State
- Capital: Umuahia
- Economic Activities: Known for oil production, agriculture, and commerce.
- Notable Features: Abia State, located in the southeastern part of Nigeria, contributes significantly to Nigeria’s oil production. It is also known for the city of Aba, an industrial hub famous for locally made textiles, leather products, and machinery.
- Environmental Challenges: Oil pollution and land degradation affect the rural parts of Abia, impacting agriculture and water resources.
2. Akwa Ibom State
- Capital: Uyo
- Economic Activities: Primarily oil and gas production, fishing, and agriculture.
- Notable Features: Akwa Ibom is one of Nigeria’s highest oil-producing states and a key contributor to the national economy. It is also known for beautiful landscapes, beaches, and a rich cultural heritage, including the Ibibio and Annang ethnic groups.
- Environmental Challenges: Oil spills, gas flaring, and pollution have led to habitat loss and health issues for local communities.
3. Bayelsa State
- Capital: Yenagoa
- Economic Activities: Oil production, fishing, and farming.
- Notable Features: Bayelsa is the least populated state in Nigeria but is crucial in terms of oil production, being home to some of Nigeria’s oldest oil fields. It has a largely riverine and mangrove-filled landscape with dense creeks and swamps.
- Environmental Challenges: Bayelsa faces severe environmental pollution, including oil spills that have drastically affected the local ecosystems and fishing livelihoods.
4. Cross River State
- Capital: Calabar
- Economic Activities: Timber, agriculture (especially cocoa and palm oil), and tourism.
- Notable Features: Cross River is renowned for its biodiversity, including the Cross River National Park and Afi Mountain Wildlife Sanctuary. The state is rich in forests and is a key area for Nigeria’s conservation efforts.
- Environmental Challenges: Deforestation and limited oil activities compared to other Niger Delta states, but growing environmental concerns regarding land use and urban expansion.
5. Delta State
- Capital: Asaba
- Economic Activities: Oil and gas production, agriculture, and petrochemicals.
- Notable Features: Delta is one of Nigeria’s largest oil-producing states and is home to the Urhobo, Itsekiri, Ijaw, Isoko, and Anioma ethnic groups. The state’s diverse landscape includes rivers, mangroves, and swamps.
- Environmental Challenges: Delta State faces issues with oil pollution, gas flaring, and social unrest due to disputes over resource control and environmental degradation.
6. Edo State
- Capital: Benin City
- Economic Activities: Agriculture, oil production, and rubber.
- Notable Features: Known for its historical significance, Edo State is home to the ancient Benin Kingdom and has a rich cultural heritage. The state has oil reserves and contributes to the regional oil output.
- Environmental Challenges: While oil production in Edo is lower than in other Niger Delta states, the state still experiences environmental pressures, particularly related to deforestation and land degradation.
7. Imo State
- Capital: Owerri
- Economic Activities: Oil production, agriculture, and commerce.
- Notable Features: Imo State, located in southeastern Nigeria, is another oil-producing state in the Niger Delta. Known for its vibrant culture and festivals, the state has a mix of urban and rural communities.
- Environmental Challenges: Oil pollution and deforestation are prominent issues, affecting agriculture and rural development.
8. Ondo State
- Capital: Akure
- Economic Activities: Oil production, cocoa, and other cash crops.
- Notable Features: The only southwestern state in the Niger Delta, Ondo is a significant producer of cocoa and rubber as well as oil. The state has a diverse terrain, including coastal areas and tropical forests.
- Environmental Challenges: Oil-related pollution affects the coastal areas, while deforestation and soil erosion are growing concerns for the agricultural sectors.
9. Rivers State
- Capital: Port Harcourt
- Economic Activities: Oil and gas production, fishing, and petrochemicals.
- Notable Features: Rivers State is the heart of Nigeria’s oil industry and hosts numerous multinational oil companies. Port Harcourt, the state capital, is a major industrial and economic hub, sometimes referred to as the “Oil Capital” of Nigeria.
- Environmental Challenges: Severe pollution from oil spills and gas flaring, combined with air and water pollution, has led to health issues and environmental degradation in many communities.