Fort Jesus stands as the most iconic and popular tourist destination in Mombasa, Kenya. Built in the late 16th century by the Portuguese, the fort is a symbol of the rich, multifaceted history that defines this coastal city. Over the centuries, the fort has witnessed the rise and fall of various powers, each leaving a distinct mark on its structure and story. Today, Fort Jesus serves as a museum, inviting visitors to explore a world shaped by trade, colonialism, and the interaction of diverse cultures.
The Strategic Location of Fort Jesus
The location of Fort Jesus is a critical element of its historical importance. Perched along the coastline near Mombasa’s Old Town, the fort was ideally placed to protect the city from naval invasions and to control the crucial Indian Ocean trade routes. Mombasa’s natural harbor made it a key point for traders, particularly during the 16th and 17th centuries, when the Portuguese sought to dominate the spice trade.
History of Fort Jesus
Fort Jesus was constructed between 1593 and 1596 under the orders of King Philip I of Portugal. Its primary function was to safeguard the Portuguese stronghold in Mombasa and the surrounding East African coast. The fort was a pivotal military structure in their efforts to control trade routes between the East and West. However, control of Fort Jesus was not always stable, as it changed hands several times over the centuries, first to the Omani Arabs, then later to the British during the colonial period.
Architectural Features of Fort Jesus
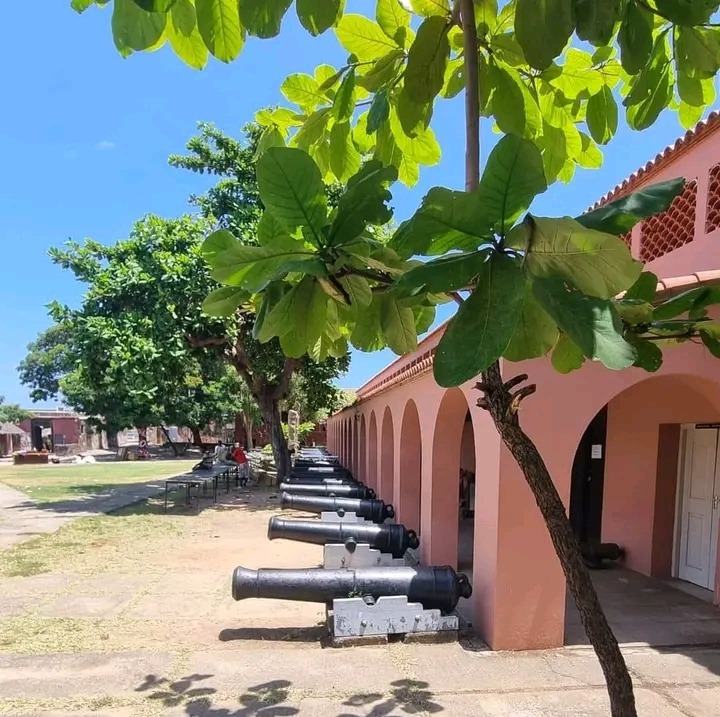
Fort Jesus is an outstanding example of Renaissance military architecture, blending elements of both European and Swahili styles. The fort is built in the shape of a man, a feature that symbolizes the king’s power. The structure, with its thick walls and bastions, was designed to resist attacks from both land and sea. Inside the fort, various courtyards, tunnels, and a chapel provide insight into the daily lives of those who lived and worked there. The architecture reflects not only military needs but also the influence of various cultures that came into contact with the Portuguese.

The Portuguese Influence in Mombasa
Fort Jesus is perhaps the clearest testament to Portuguese influence in Mombasa. The fort symbolized their dominance over the Indian Ocean and their attempts to control the lucrative spice and ivory trade. This era saw the introduction of new architectural techniques, weaponry, and even religious influences as the Portuguese established themselves along the Swahili coast.
Fort Jesus in the Slave Trade Era
During the height of the transatlantic slave trade, Fort Jesus played a significant role as a strategic point for traders. Slaves were captured from inland areas and brought to the coast, where they were sold and shipped to the Americas and other destinations. Fort Jesus acted as a holding point for these enslaved people, as well as a storehouse for commodities like spices and ivory, which were traded alongside human lives.

Fort Jesus as a Museum Today
Today, Fort Jesus is no longer a military outpost but a museum that preserves the history of Mombasa and the broader region. The museum, managed by the National Museums of Kenya, houses a diverse collection of artifacts from different eras of the city’s history. These include ceramics, pottery, tools, and weapons from the various groups that have lived and traded in Mombasa.
Artifacts Displayed at Fort Jesus Museum
The museum’s exhibits range from items related to the slave trade to maritime artifacts, illustrating the importance of seafaring and trade to Mombasa’s development. Among the most significant are Portuguese cannons, Omani swords, and Swahili cultural artifacts. These items help visitors understand the complex history of the region, including its involvement in global trade networks.
The Role of Seafarers in Mombasa’s History
Seafarers from Europe, the Middle East, and Asia frequently visited Mombasa, influencing the local culture and economy. Mombasa’s strategic location made it a key port for maritime trade, linking the Swahili coast to places as far as India, Persia, and China. Fort Jesus was a focal point in this network, offering protection to traders and serving as a warehouse for goods.
Mombasa as a Trading Hub in the 16th Century
During the period when Fort Jesus was constructed, Mombasa was a bustling trading hub. The Portuguese sought to control the city to secure their place in the spice trade, which was dominated by Arab and Indian merchants. Fort Jesus played a crucial role in this, as it allowed the Portuguese to exert influence over the region’s commerce.
Cultural Impact of Fort Jesus on Mombasa
Fort Jesus had a profound influence on the cultural landscape of Mombasa. The fort introduced European architectural styles to the region, which blended with existing Swahili designs. This fusion of cultures can still be seen in Mombasa’s Old Town, where traditional Swahili homes stand alongside colonial-era buildings.
Fort Jesus Under Different Powers
While initially built by the Portuguese, Fort Jesus did not remain in their control for long. In 1698, after a prolonged siege, the fort fell to Omani forces, marking the end of Portuguese dominance in the region. The fort later came under British control in the 19th century, reflecting Mombasa’s changing political landscape.
Restoration and Preservation of Fort Jesus
In recent years, efforts have been made to preserve Fort Jesus as both a historical monument and a tourist attraction. The National Museums of Kenya has undertaken several restoration projects to maintain the fort’s structure and its exhibits. These efforts have been crucial in ensuring that future generations can learn from and appreciate this remarkable piece of history.
Visiting Fort Jesus: What to Expect
Tourists visiting Fort Jesus today can explore its historical significance through a range of exhibits and guided tours. The fort is open to the public, with well-preserved sections including the original walls, cannons, and underground tunnels. Visitors can also view the exhibits in the museum, which include displays on the fort’s military history and Mombasa’s role in the Indian Ocean trade.
Fort Jesus and UNESCO World Heritage Status
In 2011, Fort Jesus was designated a UNESCO World Heritage site, recognizing its outstanding cultural and historical significance. This status has helped boost tourism to Mombasa, drawing visitors from around the world who are interested in exploring the rich history of the East African coast.
Nearby Attractions: Exploring Old Town
After visiting Fort Jesus, tourists can explore Mombasa’s Old Town, a historic district that offers a glimpse into the city’s past. The narrow streets, lined with Swahili houses, shops, and mosques, provide a striking contrast to the grandeur of the fort.