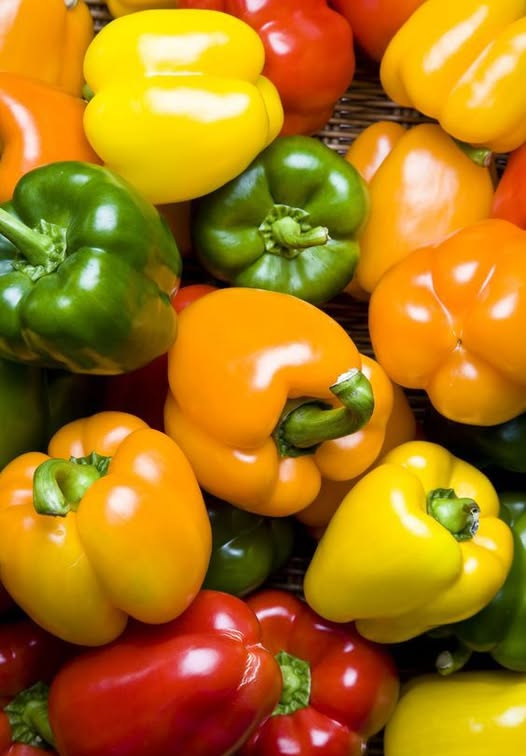
Growing peppers can be both rewarding and profitable when done with the right techniques. Peppers thrive under proper care and favorable growing conditions. This comprehensive guide outlines the key steps to get started with pepper farming.
1. Soil Preparation
Healthy soil is the foundation for a thriving pepper crop.
- Soil Testing:
- Test your soil to determine nutrient levels and pH.
- Ideal pH range: 6.0 to 6.8 for optimal pepper growth.
- Adding Organic Matter:
- Enrich the soil with compost or well-rotted manure.
- This improves soil fertility, structure, and water retention.
- Tilling:
- Loosen the soil to a depth of 15–20 cm (6–8 inches).
- Tilling allows better root penetration and aeration.
2. Seed Selection
Choosing the right seeds is crucial for a successful harvest.
- Variety Selection:
- Opt for pepper varieties suited to your climate and farming goals (e.g., bell peppers, chili peppers, or specialty varieties).
- Look for disease-resistant types to minimize crop loss.
- Certified Seeds:
- Purchase certified organic or high-quality seeds to ensure better germination rates and healthier plants.
3. Planting
Timing:
- Start seeds indoors 8–10 weeks before the last frost.
- Transplant seedlings outdoors when soil temperatures consistently stay above 18°C (65°F).
Spacing:
- Seedlings: Space plants 45–60 cm (18–24 inches) apart.
- Rows: Maintain 60–90 cm (24–36 inches) between rows for proper airflow and ease of maintenance.
Planting Depth:
- Plant seedlings deep enough so the first set of true leaves is just above the soil line.
4. Watering
Peppers require consistent watering for healthy growth.
- Consistent Moisture:
- Keep the soil evenly moist, especially during germination and early growth stages.
- Irrigation Methods:
- Use drip irrigation or soaker hoses to deliver water directly to the roots, preventing overwatering and fungal diseases.
- Mulching:
- Apply a layer of organic mulch (e.g., straw or wood chips) around the plants.
- This retains soil moisture and minimizes weed growth.
5. Fertilization
Before Planting:
- Incorporate 2–3 kg (4–6 lbs) of compost or well-rotted manure per square meter into the soil to provide a nutrient-rich base.
During Growth:
- Side-dress plants with additional compost or organic fertilizers, such as fish emulsion or seaweed extract, during the growing season to support plant development and fruit production.
6. Weed Management
Effective weed control ensures that your peppers get the nutrients and water they need.
- Mulching:
- Spread organic mulch around plants to suppress weed growth and conserve soil moisture.
- Manual Weeding:
- Regularly remove weeds by hand or use a hoe to prevent competition for resources.
Additional Tips for Successful Pepper Farming
- Pest and Disease Control:
- Watch for common pests such as aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies.
- Use natural pest control methods like neem oil or introduce beneficial insects (e.g., ladybugs).
- Staking:
- Support plants with stakes or cages to prevent them from toppling under the weight of heavy fruits.
- Pruning:
- Remove lower leaves and suckers to improve airflow and direct energy to fruit production.
- Harvesting:
- Harvest peppers when they reach the desired size and color.
- Use scissors or a knife to avoid damaging the plant.