Papaya is a versatile and rewarding crop that thrives with proper management. This guide outlines the essential steps for successfully planting and managing dwarf papaya to achieve high yields and quality fruit.
1. Soil Requirements
Papaya adapts to a variety of soils but performs best under the following conditions:
- Optimal Soil Type: Light, well-aerated, and humus-rich soil.
- pH Levels: Between 6 and 7 for healthy growth.
- Drainage: Essential to prevent waterlogging, as papaya roots are sensitive to excessive moisture.
- Ideal Soil Texture: Sandy-loamy soil is preferred, while heavy, clayey soils are less suitable.
Preparation Tips:
- Test soil pH before planting and amend it as necessary.
- Incorporate organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve fertility and drainage.
2. Propagation by Seeds
Papaya is commonly propagated through seeds. Follow these steps for effective seed management:
- Seed Germination:
- Seeds take 15–20 days to germinate.
- Seedling Growth:
- Allow seedlings to grow until they reach 20–40 cm before transplanting.
- Transplanting:
- Choose healthy, robust seedlings for transplanting.
- Transplant them to the field when they are strong enough to withstand outdoor conditions.
3. Spacing and Plant Density
Proper spacing ensures good airflow, reduces disease, and supports healthy growth:
- Large Varieties:
- Space plants 2 to 3 meters apart.
- Approximately 1,500 plants per hectare.
- Dwarf Varieties:
- Use a 2-meter spacing for around 2,500 plants per hectare.
- Alternative Spacing:
- For double quinconse lines, space rows 1.5 m apart and maintain 2.5 m between the plants in a row.
Planting Technique:
- Dig planting holes measuring 0.50 x 0.50 x 0.50 m.
- Fill the holes with a mixture of soil and organic compost before planting.
4. Fertilization
Papaya is a nutrient-intensive crop that responds well to fertilizers, especially organic ones.
Organic Fertilization:
- Apply 50 kg of good-quality compost per tree annually to maintain high productivity.
Chemical Fertilization:
- Perform soil analysis to determine the exact fertilizer requirements.
- Nitrogen (N): Promotes vigorous foliage growth.
- Phosphorus (P): Encourages root development and enhances fruit sweetness.
- Potassium (K): Improves fruit quality and starch-to-sugar transformation.
Boron Deficiency:
- Papaya is sensitive to boron deficiency, which manifests as:
- Distorted and bumpy fruits.
- Yellowing foliage.
- Gradual tree decline.
- Use boron supplements if symptoms appear.
5. Water Management
- Papaya requires consistent but moderate watering.
- Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot.
- Ensure irrigation systems provide even moisture distribution.
6. Disease and Pest Control
- Common Pests: Aphids, fruit flies, and whiteflies.
- Diseases: Powdery mildew, anthracnose, and viral infections.
- Implement integrated pest management (IPM) techniques:
- Regular monitoring for early detection.
- Use of biological controls and approved pesticides as needed.
7. Training and Pruning
- Remove damaged or diseased leaves regularly.
- Prune to shape the tree and improve light penetration.
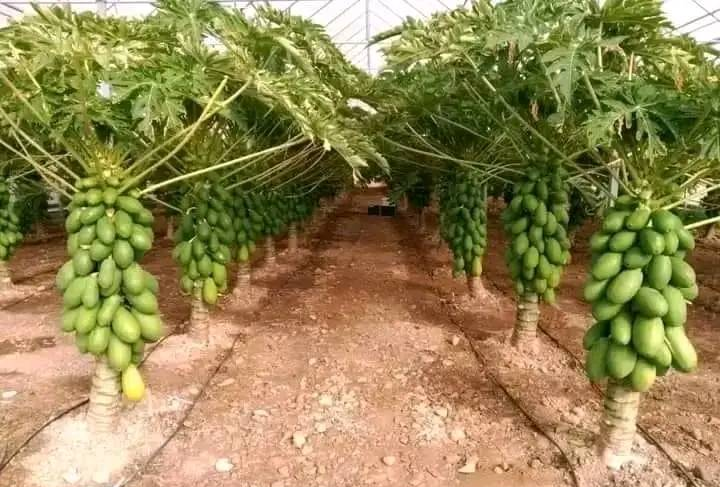

8. Harvesting
- Harvest fruits when they begin to show color changes (yellowing) for the best flavor.
- Handle fruits carefully to avoid bruising.