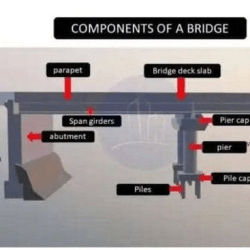
The Standard Grain Reserve (SGR) Silo System flow chart showcases the intricate coordination of multiple components to create a highly efficient grain storage and handling process. By focusing on seamless integration, automation, and quality control, silo complexes play a critical role in agricultural supply chains, ensuring food security and economic stability.
The typical SGR Silo System flow chart below, gives an insight into the main key components of the silo complexes.
Silo Complex Layout: Key Components and System Flow
A silo complex is an integrated storage system designed for the efficient handling, storage, and processing of agricultural grains and other commodities. The Standard Grain Reserve (SGR) Silo System flow chart provides a structured overview of the critical components and operational flow within such complexes. Here, we break down the essential elements and their functions, highlighting their significance in optimizing the storage and distribution process.
1. Grain Reception Area
This is the entry point for raw grain materials into the silo system.
- Weighbridges: Installed at entry points to measure the weight of incoming and outgoing grain trucks.
- Unloading Platforms: Equipped with conveyor belts or hydraulic tippers to facilitate efficient offloading.
- Primary Inspection Zone: Where quality checks for moisture content, contaminants, and weight are conducted before storage.
2. Pre-Cleaning Section
Before grains are stored, they undergo pre-cleaning to remove impurities.
- Pre-Cleaners: Machines that remove large debris, dust, and other contaminants.
- Screening Mechanisms: Use sieves and separators to grade the grains based on size and quality.
- Magnetic Separators: Eliminate metal particles that could damage machinery during further processing.
3. Grain Elevators and Conveyors
To move grains efficiently throughout the complex, a system of elevators and conveyors is essential.
- Bucket Elevators: Vertical conveyors used for transporting grains to higher storage bins.
- Chain Conveyors: Move grains horizontally between sections with minimal spillage.
- Inclined Belt Conveyors: Transport grains between different levels of the facility.
4. Storage Silos
The silos are the central feature of the complex, designed for long-term grain storage.
- Types of Silos:
- Flat-Bottom Silos: Ideal for bulk storage over extended periods.
- Hopper-Bottom Silos: Enable quick unloading and are suitable for short-term storage.
- Ventilation Systems: Maintain temperature and humidity levels to prevent spoilage.
- Aeration Equipment: Promotes airflow to avoid mold growth and preserve grain quality.
- Temperature Monitoring Sensors: Continuously track internal conditions to ensure stability.
5. Drying and Conditioning Units
These units prepare grains for storage by reducing moisture content.
- Drying Units: Remove excess moisture using heated air, ensuring grains are safe for long-term storage.
- Conditioning Systems: Adjust grain temperature and moisture to the ideal storage level.
6. Grain Processing Section
Some silo complexes integrate grain processing facilities to enhance value.
- Milling Units: Grind grains into flour or other by-products.
- Packaging Stations: Bag processed grains for retail or distribution.
- By-Product Collection: Systems for gathering husks, bran, or other by-products for further use.
7. Loading and Dispatch Area
After storage or processing, grains are prepared for distribution.
- Weighing Systems: Ensure accurate measurements before dispatch.
- Loading Bays: Use bulk loading systems or conveyor belts for seamless transfer to trucks.
- Quality Control Stations: Conduct final inspections to verify the grain meets export or market standards.
8. Utility and Control Rooms
These ensure the smooth operation of the entire silo complex.
- Control Systems: Centralized monitoring for temperature, humidity, grain movement, and machine operations.
- Backup Power Generators: Maintain operations during power outages.
- Fire Safety Systems: Include alarms, sprinklers, and fireproof coatings to protect the facility.
System Flow Chart
Below is a simplified depiction of the silo system’s operational flow:
- Grain Reception → Pre-Cleaning → Elevators/Conveyors → Storage Silos
- Optional: Drying/Conditioning → Grain Processing → Packaging
- Storage Silos → Dispatch Area (Loading/Distribution)

Benefits of a Well-Designed Silo Complex
- Efficient Grain Handling: Reduces time and labor costs.
- Preservation of Quality: Maintains grain condition for long durations.
- Scalability: Can handle both small-scale and large-scale operations.
- Environmental Protection: Minimizes waste and reduces the carbon footprint through efficient systems.