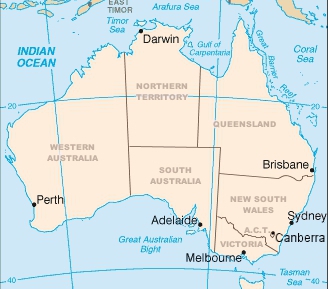
Australia is divided into 6 states and 10 territories (2 internal + several external).
1. States of Australia
Each state has its own parliament, governor, and premier.
| State | Abbrev. | Capital | Population (2024) | Area (km²) | Premier (Party) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New South Wales | NSW | Sydney | 8.51M | 800,150 | Chris Minns (Labor) |
| Victoria | VIC | Melbourne | 7.01M | 227,416 | Jacinta Allan (Labor) |
| Queensland | QLD | Brisbane | 5.61M | 1,729,742 | David Crisafulli (Liberal Nat.) |
| Western Australia | WA | Perth | 2.98M | 2,527,013 | Roger Cook (Labor) |
| South Australia | SA | Adelaide | 1.88M | 984,321 | Peter Malinauskas (Labor) |
| Tasmania | TAS | Hobart | 576K | 68,401 | Jeremy Rockliff (Liberal) |
2. Internal Territories
Directly governed under federal law (though ACT and NT have local parliaments).
| Territory | Capital | Population (2024) | Area (km²) | Chief Minister |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australian Capital Territory (ACT) | Canberra | 476K | 2,358 | Andrew Barr (Labor) |
| Northern Territory (NT) | Darwin | 256K | 1,347,791 | Lia Finocchiaro (Country Liberal) |
| Jervis Bay Territory | Jervis Bay Village | 405 | 67 | Administered federally |
3. External Territories
Mostly small, remote islands. Some have local councils, others are uninhabited.
- Norfolk Island – Kingston (Pop. ~2,600), has local council but integrated into NSW.
- Christmas Island – Flying Fish Cove (Pop. ~1,900).
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands – West Island (Pop. ~550).
- Coral Sea Islands – Very small population (only staff on Willis Island).
- Ashmore & Cartier Islands – Uninhabited.
- Heard Island & McDonald Islands – Uninhabited, sub-Antarctic.
- Australian Antarctic Territory – Pop. ~60 (scientists at Davis Station).
4. Former Territories
- Central Australia & North Australia (1926–1931) – later merged into today’s NT.
- Papua & New Guinea – Australian-administered until independence (1975).
- Nauru – Administered until independence (1968).
✅ Key Point:
- States have more power (self-governing, entrenched in the Constitution).
- Territories are under federal control (powers granted and can be withdrawn).