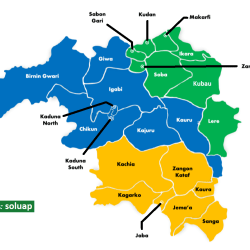
The 23 Local Government Areas in Kaduna State are:
- Ikara
- Kubau
- Kudan
- Lere
- Makarfi
- Sabon Gari
- Soba
- Zaria.
- BirninGwari
- Chikun
- Giwa
- Igabi
- Kaduna North
- Kaduna South
- Kajuru
- Jaba
- Jema’a
- Kachia
- Kagarko
- Kaura
- Kauru
- Sanga
- Zangon Kataf
Kaduna State
Kaduna is a state in Nigeria. The capital and largest city is also called Kaduna
The city was the capital of Northern Nigeria region.
Kaduna is located in north-western Nigeria besides River Kaduna, a major tributary of the Niger River.
It is a trade centre and a major transportation hub. It serves as a gateway to several northern Nigeria locations.
Kaduna state was created on
27 May 1967
It’s total land area is
46,053 km2
Population (2020 est.)
9.48M

Kaduna state’s 23 local government areas are
- Ikara
- Kubau
- Kudan
- Lere
- Makarfi
- Sabon Gari
- Soba
- Zaria.
- BirninGwari
- Chikun
- Giwa
- Igabi
- Kaduna North
- Kaduna South
- Kajuru
- Jaba
- Jema’a
- Kachia
- Kagarko
- Kaura
- Kauru
- Sanga
- Zangon Kataf
Senatorial districts
Kaduna North
Kaduna Central
Kaduna South
Senatorial districts & their local government areas
- Kaduna North
Ikara, Kubau, Kudan, Lere, Makarfi, Sabon Gari, Soba, and Zaria. - Kaduna Central
Birnin Gwari, Chikun, Giwa, Igabi, Kaduna North, Kaduna South, and Kajuru. - Kaduna South
Jaba, Jema’a, Kachia, Kagarko, Kaura, Kauru, Sanga, and Zangon Kataf.①

Kaduna state’s nickname “Centre of Learning” is because of it being home to a number of institutions of learning like Ahmadu Bello University (ABU), Nigerian Defense Academy (NDA), Nigerian College of Aviation, Zaria, Barewa College among others.
Ethnicities
Gbagyi
Adara
Atyap
Ham
Kanuri
Nupe
among others
The Ham tribe (in Southern Kaduna state) is attributed with the Nok culture and terracotta.
Nok is one of Africa’s earliest civilizations.
Vegetation
Savannah woodlands
Major crops
Maize, Millet, Rice, Ginger and Sorghum.
Solid minerals
Iron-Ore, Gold, Gemstones, Granite, and Marbles.②
The word Kaduna is said to be a corruption of the Hausa word Kaddani meaning ‘crocodiles’ (kaduna being the plural). Another version of the name says it’s the Gbagyi word ‘Odna’, meaning ‘river’.
Frederick Lugard, the first British governor of Northern Nigeria, chose the site due to its proximity to the Lagos-Kano Railway. Building began in 1913.
In 1917 Kaduna replaced Zungeru, 100 miles (160 km) southwest, as the capital of the Northern Provinces.
It also served as capital of the Northern Region from 1954 to 1967.
The city is influential being the headquarters of several political, military and cultural organizations especially in northern Nigeria.
Since the late 1950s, Kaduna had become a major industrial, commercial, and financial city in northern states of Nigeria.
Industries are located south of the Kaduna River near the main railway junction.
Kaduna has cotton-textile spinning and weaving mills; knit fabrics are also produced in Kaduna.

The food industry produces beer, soft drinks, baked goods, and processed meat. Light manufactures include leather goods, plastics, ceramics, pharmaceuticals, furniture, and televisions; and there are several printing and publishing firms.
The city’s heavy industries make steel and aluminum products, cement, asbestos cement, concrete blocks, electrical motors, ordnance, and explosives.
There are a steel-rolling plant, an automobile assembly factory, and an oil refinery (supplied by an oil pipeline from the Niger delta oil fields).
A petrochemicals plant began operations in the early 1980s. Kaduna is also a centre for the construction industry. The city serves as a collecting point for cotton, peanuts (groundnuts), shea nuts, and hides and skins; there is also a considerable local trade in sorghum, millet, corn (maize), kola nuts, goats, poultry, and cattle.
A 2009 World Bank survey states that Kaduna is one of the top six cities with the highest unemployment. 20% of the population was estimated to be unemployed.
By air transport the city is served by Kaduna International Airport. The airport commenced operations in 1982.
Kaduna is also on the route of the Lagos–Kano Standard Gauge Railway, which has been completed between the national capital of Abuja and Kaduna. Trains for Abuja depart from the Rigasa Railway Station in Kaduna.