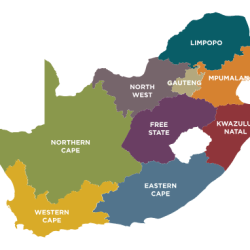
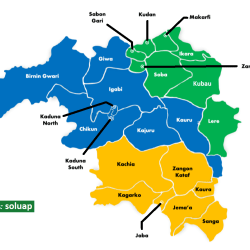
Nok civilization
• 600 BCE–200 CE
Evidence of Nok civilization.
Establishment of some kingdoms
• 900–1000 CE
Establishment of Hausa Kingdoms, Benin Kingdom, Kanem–Bornu Empire, and the Oyo Empire.
Height of trans-saharan trade
• 1300–1600
Height of the trans-Saharan trade, Oyo Empire, and the Sefawa Dynasty in northeastern Nigeria.
Portuguese traders visit the Bight of Benin
• 1472
Joao Alfonso d’Alveiro visits Benin
• 1485
Joao Alfonso d’Alveiro visits Benin Kingdom and invites the King Ozolua to Portugal.
Olaudah Equiano’s narrative
• 1789
The first printing of Olaudah Equiano’s narrative took place.
Mungo Park explores the Niger River
• 1797–1806
Hugh Clapperton travels across Nigeria
• 1822–1826
Hugh Clapperton travels across Nigeria and records his encounters with royalty.
Legitimate international trade begins in the hinterland by way of the Niger River
• 1830
Final collapse of the Oyo Empire.
• 1833
First Anglican Church Missionary
• 1841
The first Anglican Church Missionary Society members arrive in Nigeria during an expedition on the Niger River.
First Christian mission at Badagry
• 1842
The Wesleyan Methodist Missionary Society establishes the first Christian mission at Badagry.
Christian mission at Abeokuta.
• 1846
The Anglican Church Missionary Society establishes a Christian mission at Abeokuta.
First British diplomatic outpost at Lagos
• 1851
John Beecroft establishes the first British diplomatic outpost at Lagos.
Nigeria’s first newspaper, Iwe Ihori
• 1859
The circulation of Nigeria’s first newspaper, Iwe Ihorin, which was written in Yoruba.
Yoruba Wars
• 1859–1893
The Yoruba Wars, including the Ijayi War.
Lagos Colony established
• 1861
The British seize Lagos from King Dosumu and establish the Lagos Colony.
George Goldie starts the United African Company
• 1879
The United African Company changes its name to the National Africa Company
• 1882
Oil Rivers Protectorate is established
• 1884
National Africa Company becomes the Royal Niger Company
• 1886
The National Africa Company becomes the Royal Niger Company upon receipt of a royal charter from the British government.
British claim territories in northern Nigeria
• 1890
The British claim territories in northern Nigeria through the Anglo–French Agreement.
Treaty between the British and the King of Benin
• 1892
The Gallwey Treaty between the British and the King of Benin is signed.
Oil Rivers Protectorate changes
• 1893
The Oil Rivers Protectorate becomes the Niger Coast Protectorate.
Akassa Massacre
• 1895
The Akassa Massacre in the Niger Delta involving the people of Brass and the Royal Niger Constabulary.
Hope Waddell Training Institute
• 1895
The founding of the Hope Waddell Training Institute at Calabar.
The name “Nigeria” is officially adopted.
• 1897
Protectorate of Northern Nigeria and the Protectorate of Southern Nigeria
• 1899 December
The establishment of the Protectorate of Northern Nigeria and the Protectorate of Southern Nigeria.
Royal Niger Company’s charter revoked
• 1900
The British revoke the Royal Niger Company’s charter and combine the Niger Coast Protectorate with nearby areas to form the Protectorate of Southern Nigeria. Likewise, areas in the North become the Protectorate of Northern Nigeria.
Sokoto Caliphate conquered
• 1903
The British conquer and take the Sokoto Caliphate.
The Niger Traders’ Association formed.
• 1909
The founding of King’s College, Lagos.
• 1909 September
Frederick Lugard is appointed governor
• 1912
Sir Frederick Lugard is appointed governor of the protectorates.
The amalgamation of the protectorates.
• 1914
The British recruit Nigerian troops during World War I.
• 1914–1918
Coal mining begins at Enugu
• 1915
The Lagos Town Council is established
• 1917
The Clifford Constitution is implemented
• 1922
West African Students’ Union founded
• 1925
Ladipo Solanke forms the West African Students’ Union in London.
Daily Times began
• 1926 June
The Daily Times, Nigeria’s first English-language newspaper, begins circulation.
Aba Riots occurred
• 1929
Aba Riots occurred in southeastern Nigeria.
Advent of the Aladura churches
• 1932
The advent of the Aladura churches and Yaba Higher College.
The Lagos Youth Movement is formed
• 1934
The Nigerian Youth Movement is founded
• 1936
Shell begins oil exploration
• 1937
Shell–D’Arcy Exploration Company begins oil exploration in the Niger Delta.
Ahmadu Bello receives the ceremonial title of sardauna
• 1938
Southern Nigeria is divided into Eastern and Western provinces
• 1939
The British recruit troops during World War II
• 1939–1945
Railway Workers’ Union started
• 1940 January
Chief Michael Imoudu forms the Railway Workers’ Union.
The National Council of Nigeria and the Cameroons is created
• 1944
General Strike by Nigeria’s labor unions
• 1945 June–August
Implementation of the Richardson Constitution and the creation of three regions
• 1946 January
University College of Ibadan is founded.
• 1947
The Northern People’s Congress is created
• 1949
Action Group founded
• 1950 March
Chief Obafemi Awolowo creates the Action Group.
The Macpherson Constitution is implemented
• 1951
First general elections
• 1952
Nigeria holds its first general elections.
Constitutional conference
• 1953
Nigeria’s three major political parties attend a constitutional conference to discuss the adoption of a federal constitution and allowance of self-government for any region desiring it.
The Eastern Regional government crisis occurs
• 1953 January
Kano Riots occurred
• 1953 May
Kano Riots take place in the midst of intense political campaigning.
The Lyttleton Constitution is implemented.
• 1954
Universal Primary Education program in Western Region
• 1955
Chief Obafemi Awolowo launches the Universal Primary Education program in Western Region.
Commercial quantities crude oil discovered in the Niger Delta
• 1956
The Shell–BP Petroleum Company discovers commercial quantities of petroleum in the Niger Delta.
The Mid-West Movement agitates for the creation of the Mid-Western Region
• 1956
Black Orpheus begins publication
• 1957
The British launch the Willink Commission on minority groups
• 1957 September
The Eastern and Western Regions declare self-rule
• 1957 September
The establishment of the Nigerian Broadcasting Corporation
• 1957 April
The first batch of petroleum is exported
• 1958
Susanne Wenger and her colleagues start the New Sacred Art Movement
• 1958
The Northern Region declares self-rule
• 1959
The Central Bank of Nigeria is established
• 1958
Nigeria holds its elections in preparation for independence
• 1959 December
Nigeria becomes independent
• 1960 October
Nigeria joins the British Commonwealth
• 1960 May
University of Lagos and Ahmadu Bello University in Zaria are established
• 1962
The Action Group Crisis erupts in the Western Region
• 1962
Nigeria’s first population census is held, but the results are not released
• 1963
A portion of the Western Region is made into the Mid-Western Region
• 1963 August
Chief Obafemi Awolowo is imprisoned on charges of felony
• 1963 September
Nigeria becomes a republic
• 1963 October
Nigeria holds elections, some boycotted
• 1964 December
Nigeria holds elections, which many people from the Western and Eastern Regions boycotted
The Western Region holds elections, which result in violence
• 1965 October
First military coup d’état occurs
• 1966 January
The first military coup d’état occurs, placing Major General Johnson Aguiyi-Ironsi as the head of state.
Aguiyi Ironsi abolishes regions, creating a centralized administrative structure
• 24 May 1966
Northerners reject Aguiyi-Ironsi’s removal of regions and engage in violent attacks on southerners, mainly Igbo, living in north
• May 1966
Northern officers launch the second military coup d’état and place General Yakubu Gowon as the head of state
• 29 July 1966
Chukwuemeka Ojukwu, governor of the Eastern Region, rejects Gowon’s authority
• August 1966
Aburi Conference held
• 1967 January
The Aburi Conference is held, but not successful.
Nigeria became a country with 12 states
• May 1967
Gowon transforms Nigeria’s four regions into 12 states.
Later Ojukwu declares the Eastern Region independent and renames it the Republic of Biafra.
The civil war begins
• July 1967
Mid-Western Region declared independent
• 19–21 September 1967
The Mid-Western Region is declared independent and named the Republic of Benin.
Ojukwu presents the Ahiara Declaration
• 1969 June
Ojukwu presents the Ahiara Declaration, declaring the Republic of Biafra a socialist state. The Petroleum Decree is issued.
Peace talks are held in Kampala
• August 1969
Owerri is seized by federal forces
• 1970 7 January
Ojukwu leaves Biafra for Ivory Coast
• 11 January 1970
Biafra surrenders, ending the civil war
• 12 January 1970
Creation of the state-owned Nigerian National Oil Corporation
• 1971 April
Nigeria joins the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries
• July 1971
The national currency is switched to the naira
• January 1971
NYSC established
• June 1971
Gowon sets up the National Youth Service Corps program to promote unity.
Second census
• 1974
The second population census is taken, but the results are not released.
ECOWAS founded
• 1975 May
The Economic Community of West African States is formed.
A third military coup d’état takes place, making General Murtala Mohammed head of state
• July 1975
7 new states created
• 1976 February
Murtala Mohammed creates seven new states, bringing the number of states to 19.
Abuja creation started at plan level
• 1976 February
He also selects Abuja as the future site of Nigeria’s new capital.
Murtala Mohammed assassinated
• 13 February 1976
Murtala Mohammed was assassinated and General Olusegun Obasanjo becomes head of state.
Universal Primary Education program launched nationwide
• September 1976
Nigeria hosts the World Black and African Festival of Arts and Culture
• 1977 January–February
The Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation replaces the Nigerian National Oil Corporation as the state oil company
• April 1977
The unification of all major trade unions into one national union, called Nigerian Labour Congress
• 1978
The formation of the Okigbo Commission to assess revenue allocation
• 1979
Aspects of British Petroleum’s operations are nationalized
• August 1979
Shagari becomes president
• October 1979
Aliyu Usman Shagari is elected as president, marking the start of Nigeria’s Second Republic.
Green Revolution launched
• December 1979
Shagari launches the Green Revolution.
The Maitatsine Riots erupt in the North
• 1980 December
Pope John Paul II of the Catholic Church makes a visit to Nigeria
• 1982 12 February
SAP started
• 1983
Nigeria starts a Structural Adjustment Program.
Fourth military coup takes place, removes Shagari
• December 1983
The fourth military coup d’état takes place, removing Shagari and installing Major General Muhammadu Buhari as head of state.
This transfer of power marks the end of the Second Republic.
WAI launched
• 1984
Buhari launches his War Against Indiscipline program.
Fifth military coup takes place, removes Buhari
• 1985 August
The fifth military coup d’état ejects Buhari and installs General Ibrahim Babangida.
Wole Soyinka wins the Nobel Prize for Literature
• 1986
Babangida creates two new states, making the total number of states 21
• 1987
The Kafachan Riots erupt in Kaduna State
• March 1987
The founding of the Mass Mobilization for Self Reliance, Social Justice, and Economic Recovery program
• July 1987
SDP and NRC launched
• 1989 October
Babangida allows only two political parties— (the Social Democratic Party and the National Republican Convention) to operate in Nigeria, giving the appearance of democracy.
ECOMOG founded
• 1990 August
The Economic Community of West African States Monitoring Group (ECOMOG) is created.
Third census
• 1991
The third population census is taken, placing Nigeria’s population at 88.5 million people.
Babangida creates several new states, increasing the number of states to 30
• August 1991
Abuja replaces Lagos as Nigeria’s capital
• December 1991
MOSOP founded
• 1992
The Movement for the Survival of the Ogoni People is formed.
OMPADEC established
• July 1992
The Oil Mineral Producing Areas Development Commission is established to improve the economic situation for the inhabitants of the Niger Delta.
Presidential election cancelled
• 1993 12 June
A failed presidential election takes place, which would have marked the start of a Third Republic. Chief M. K. O. Abiola, who many identify as the winner, is accused of treason and imprisoned.
Babangida passes power to the Interim National Government
• August 1993
NADECO founded
• 1994 May
The National Democratic Coalition is formed.
Sixth military coup takes place, enthrones Abacha
• November 1994
The sixth military coup d’état ends the Interim National Government and places General Sani Abacha as the new head of state.
NHRC founded
• 1995
The National Human Rights Commission is established.
Abacha tries and imprisons several prominent politicians
• March 1995
The Oduduwa People’s Congress is formed in response to the annulled presidential elections of 1993
• August 1995
Abacha declares the transition to a civilian government in three years
• 1 October 1995
Ken Saro-Wiwa and 8 others killed
• November 1995
Ken Saro-Wiwa, along with eight other Ogoni leaders, is hanged by Abacha.
Nigeria’s membership in the Commonwealth Secretariat is suspended until 1999.
Ban on political associations lifted
• 1996 June
Abacha lifts the ban on political associations, allowing for the organization of political parties.
Abacha unveils his Vision 2010 plan
• September 1996
Abacha creates six new states, making a total of 36 states
• October 1996
The emergence of the Ijaw Youth Council
• 1998
The second wave of violent clashes between the Modekeke and Ife (a Yoruba subgroup) occurs in Ile-Ife
• January 1998
INEC formed
• 1998
The Independent National Electoral Commission is created to oversee elections.
Abacha dies
• 8 June 1998
Abacha dies and General Abdulsalami Abubakar replaces him as head of state.
Abiola dies in prison
• 7 July 1998
Abubakar facilitates Nigeria’s transition to a democratic state and allows nine registered parties to promote candidates
• 20 July 1998
The Universal Primary Education program is replaced by the Universal Basic Education program
• 1999
Nigeria’s membership in the Commonwealth Secretariat is reinstated
• 1999
Obasanjo becomes democratically elected president
• May 1999
Obasanjo becomes Nigeria’s democratically elected, civilian president, ushering in the Fourth Republic.
Zamfara State is the first state to incorporate aspects of Sharia into its criminal law
• 2000
The vigilante Bakassi Boys emerge in Anambra State
• 2000
A series of clashes between the Jukun and Tiv in Taraba State over land rights
• 2001
A massacre of an estimated 100 civilians is carried out by Nigerian soldiers in Benue State
• October 2001
Nigeria participates in the launching of New Partnership for African Development
• 2001
Twelve states, predominantly in the North, implement Sharia into their criminal law
• 2002
The International Court of Justice rules in favor of Cameroon regarding the disputed Bakassi Peninsula
• 2002
Violence between Yoruba and Hausa youths erupts in Lagos over religion
• February 2002
Phantom Crescent, a play by the Nigerian playwright Shehu Sani, is banned by a Sharia court in Kaduna State
• October 2002
Miss World Pageant riots take place in Kaduna
• November 2002
Obasanjo wins a second term as president
• 2003 May
A strike lasts nine days over the government’s increase in fuel prices
• July 2003
ECOMOG sends a military force (dominated by Nigerian soldiers) to end Liberia’s civil war
• August 2003
To facilitate this, Nigeria offers Liberia’s President Charles Taylor asylum.
With Russian assistance, Nigeria launches its first telecommunications satellite, Nig Sat 1
• September 2003
A series of national strikes over the rising price of fuel takes place
• 2004
Transparency International ranks Nigeria the second most corrupt country in the world
• 2004
A state of emergency is declared in Plateau State as a way to stop violence between Muslims and Christians
• May 2004
Nigeria receives debt relief of $18 billion by the Paris Club lenders
• 2005 July
The much criticized National Electric Power Authority company is renamed the Power Holding Company of Nigeria
• 2005
The emergence of the Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta (MEND)
• 2006 January
The kidnapping of foreign oil workers in the Niger Delta becomes a frequent occurrence
• 2006
Riots over caricatures of the Prophet Muhammad in a Danish newspaper erupt in northern Nigeria
• February 2006
Fourth census
• March 2006
The fourth population census is taken, placing Nigeria’s population at 140 million. Nigeria agrees to hand Charles Taylor over to the Liberian government
Nigeria’s Senate rejects Obasanjo’s constitutional amendment that would allow him to stand for a third term as president
• May 2006
Nigeria releases the Bakassi Peninsula to Cameron, as called for by the International Court of Justice
• August 2006
Muhammadu Maccido, the 19th sultan of Sokoto, dies in a plane crash
• October 2006
Muhammed Sa’adu Abubakar III is installed as the 20th sultan of Sokoto
• November 2006
A round of general elections takes place, tainted by flagrant fraud and corruption
• April 2006
Umaru Yar’Adua is sworn in as president, marking Nigeria’s first successful transfer of power from one elected president to another
• May 2006
MEND threatens to end a cease-fire and return to its disruptive activities
• September 2006
Transparency International ranks Nigeria as the 59th most corrupt country in the world
• 2008
Nigeria’s loss of oil production, caused by instability in the Niger Delta, reaches a record high of one-third
• June 2008