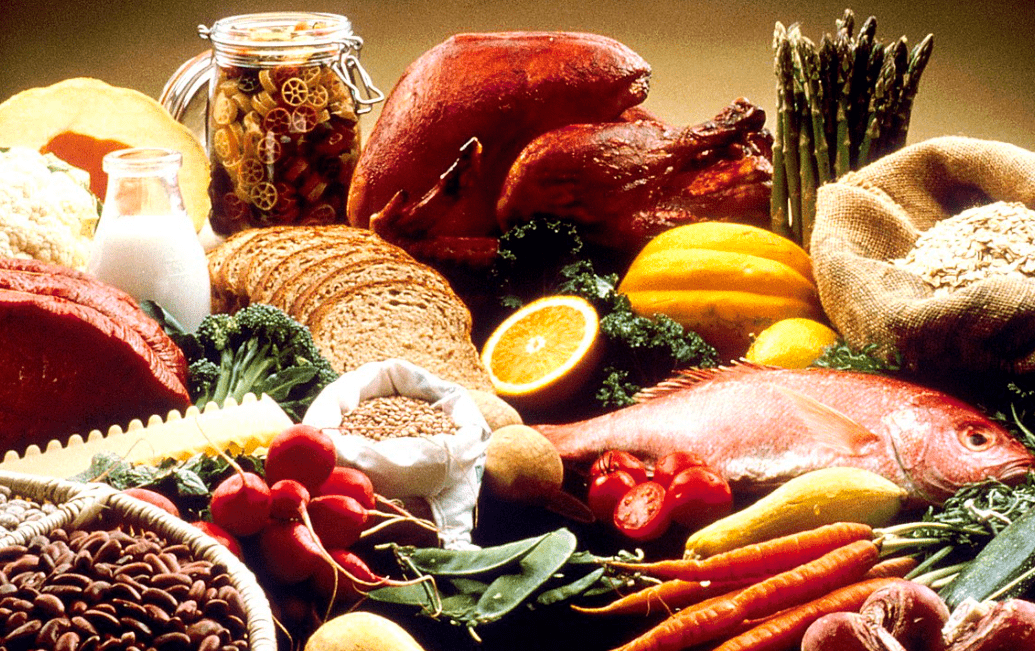
A healthy diet is the cornerstone of overall well-being, providing the nutrients and energy needed to thrive. It involves consuming a balanced mix of macronutrients, micronutrients, fiber, and water while minimizing harmful elements like excess sugar, sodium, and ultra-processed foods. A healthy diet supports physical health, mental clarity, and long-term vitality, making it essential for everyone. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the components, benefits, guidelines, and practical strategies for achieving a balanced diet.
A healthy diet isn’t about strict restrictions or deprivation—it’s about creating sustainable habits that nourish your body and mind. By focusing on balance, variety, and mindful choices, you can enjoy the benefits of better health, increased energy, and a longer, happier life. Take small steps, make gradual changes, and embrace the journey to a healthier you.
What is a Healthy Diet?
A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition, ensuring proper growth, energy, and protection against diseases. Key elements include:
- Macronutrients: Proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, which supply the majority of energy and support bodily functions.
- Micronutrients: Vitamins and minerals critical for immune function, bone health, and more.
- Hydration: Water, essential for every cell and process in the body.
- Fiber: Vital for digestive health and maintaining blood sugar levels.
A balanced diet incorporates these elements in the right proportions, emphasizing nutrient-dense foods over empty calories.
Benefits of a Healthy Diet
A nutritious diet offers numerous advantages:
- Improved Physical Health: Reduces risks of chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
- Enhanced Mental Well-Being: Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants support brain health, improving mood and cognitive function.
- Longer Life Expectancy: Balanced eating contributes to longevity by preventing degenerative diseases.
- Increased Energy Levels: Proper nutrition fuels the body, combating fatigue and boosting productivity.
Components of a Healthy Diet
Fruits and Vegetables
These are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Aim for at least 400 grams daily, excluding starchy vegetables like potatoes. Diverse colors indicate a range of nutrients.
Whole Grains
Whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice are high in fiber, aiding digestion and stabilizing blood sugar. They also provide B vitamins and essential minerals.
Protein Sources
Protein is vital for muscle repair, immune function, and hormone production. Options include:
- Animal-Based: Lean meats, fish, eggs, and dairy.
- Plant-Based: Beans, lentils, tofu, and nuts.
Healthy Fats
Not all fats are created equal. Focus on unsaturated fats found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, while avoiding trans fats and limiting saturated fats.
Hydration
Water supports digestion, nutrient transport, and temperature regulation. Adults should consume about 2–3 liters daily, adjusting for activity levels and climate.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
A healthy diet isn’t just about what you include—it’s also about what you minimize:
- Ultra-Processed Foods: High in calories, low in nutrients, and often loaded with unhealthy additives.
- Added Sugars: Excess sugar increases the risk of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Keep intake below 10% of total calories.
- Sodium: High salt intake can lead to hypertension. Limit consumption to less than 5 grams per day.
- Trans Fats: Found in some processed snacks and fried foods, they increase heart disease risk.
World Health Organization (WHO) Guidelines
The WHO offers practical recommendations for healthy eating:
- Balance Calories and Activity: Consume calories equal to what your body burns.
- Limit Fats: No more than 30% of total calories, prioritizing unsaturated fats.
- Eat Fruits and Vegetables: At least 5 portions a day, complemented by legumes, nuts, and whole grains.
- Reduce Sugar: Limit to less than 10% of daily caloric intake.
- Control Sodium: Use iodized salt but keep total intake low.
Practical Tips for Healthy Eating
Meal Planning and Preparation
- Plan weekly meals to ensure a variety of nutrients.
- Batch cook and store meals for convenience.
- Use herbs and spices for flavor instead of salt and sugar.
Portion Control
- Use smaller plates to manage portion sizes.
- Avoid distractions like TV during meals, which can lead to overeating.
Mindful Eating
- Eat slowly to enjoy your food and recognize fullness.
- Listen to your body’s hunger cues instead of eating out of habit or stress.
Overcoming Barriers to Healthy Eating
Budget Constraints
- Choose affordable, nutrient-dense options like beans, lentils, and seasonal produce.
- Reduce waste by freezing leftovers and repurposing ingredients.
Time Limitations
- Prepare quick, healthy snacks like nuts or yogurt.
- Invest in kitchen tools like slow cookers to save time.
Cravings and Indulgences
- Balance indulgences with healthy meals.
- Substitute unhealthy cravings with nutritious alternatives, like fruit for sweets.
Healthy Eating for Different Life Stages
Children and Teens
Growing bodies need ample calcium, iron, and protein for development. Encourage balanced meals and healthy snacking habits.
Adults
Focus on nutrient-dense foods to maintain energy, bone health, and prevent chronic diseases.
Elderly Individuals
Calcium, vitamin D, and protein become more critical with age to maintain bone and muscle health.
Emerging Trends in Healthy Eating
Sustainable Diets
Eco-friendly eating focuses on local, seasonal, and plant-based foods, reducing the environmental impact.
Functional Foods
Foods like probiotics and omega-3-rich options go beyond basic nutrition to support specific health benefits.
Technology in Nutrition
Apps and wearable devices help track dietary habits, offering personalized insights for healthier choices.

- What should I eat daily for a balanced diet?
A mix of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, protein, and healthy fats, accompanied by water. - How can I reduce sugar without missing it?
Opt for natural sweeteners like honey or fruit, and gradually decrease added sugar in recipes. - Can I eat healthy on a tight budget?
Yes! Prioritize affordable staples like beans, rice, and seasonal produce. Cook at home to save money. - Is it okay to skip meals?
Skipping meals can lead to overeating later. Focus on regular, balanced meals to maintain energy levels. - Do cheat days ruin a diet?
Occasional indulgences are fine. Just ensure they’re balanced with nutritious meals. - How can I get my kids to eat healthier?
Involve them in meal prep and offer a variety of colorful, appealing foods.