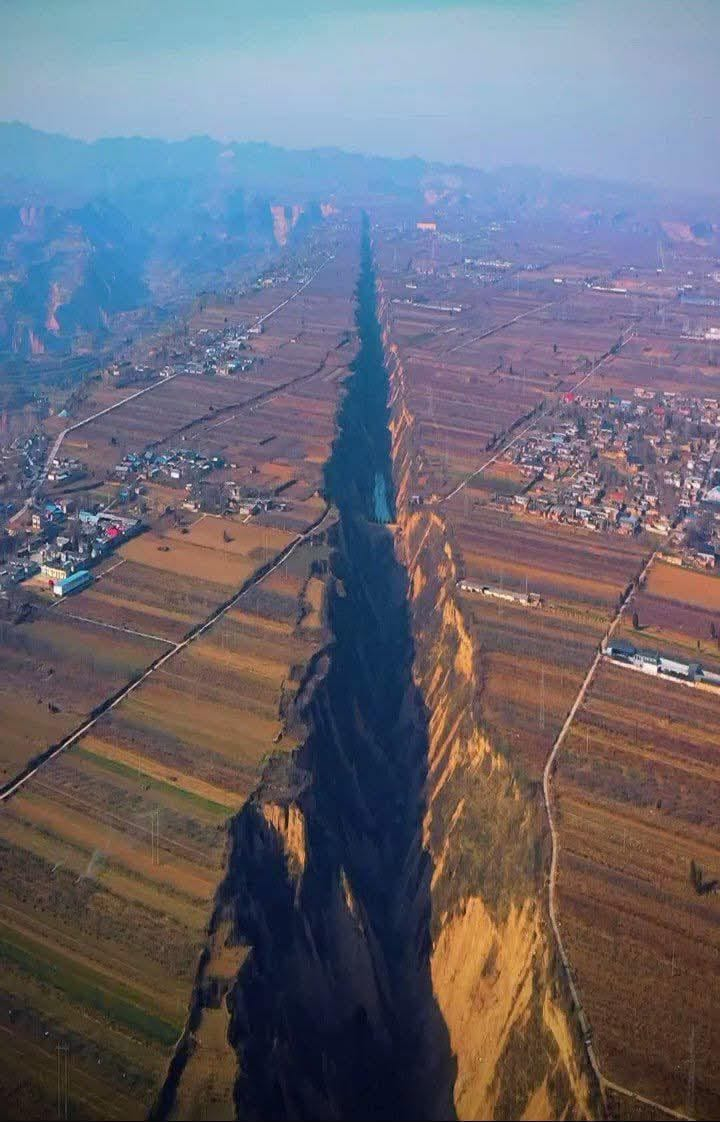
The Rift Valley in Pinglu, Shanxi Province, is a fascinating geological feature located in north-central China’s Loess Plateau. This region, renowned for its unique topography and historical significance, encompasses approximately 400,000 square kilometers of rugged terrain. Spanning about 10 kilometers in length, the Rift Valley offers insights into Earth’s dynamic processes and serves as a captivating site for geological and ecological studies.
Overview of the Loess Plateau
The Loess Plateau, where the Rift Valley is located, is a prominent geographic region characterized by its thick deposits of wind-blown silt, known as loess. Covering parts of Shanxi, Shaanxi, and other provinces, the plateau is known for:
- Historical Importance: It is considered the cradle of Chinese civilization, with a history of human settlement and agriculture dating back thousands of years.
- Unique Geology: The loess deposits are highly susceptible to erosion, creating a landscape of deep gullies and steep ridges.
Formation of the Pinglu Rift Valley
The Rift Valley in Pinglu was formed as a result of tectonic activity within the Earth’s crust. Movements of tectonic plates caused the land to fracture and form a linear depression, typical of rift valleys worldwide. Key geological aspects of the formation include:
- Tectonic Activity: Substantial forces pulling the crust apart led to the formation of the valley.
- Loess Erosion: The loess soil in the region contributes to the valley’s dynamic and evolving shape over time.
Geographical Features
Stretching over 10 kilometers, the Pinglu Rift Valley is defined by:
- Sharp Cliffs and Steep Slopes: These features highlight the valley’s tectonic origins.
- Vegetation and Soil: While the Loess Plateau is prone to erosion, parts of the valley are covered with sparse vegetation, aiding in soil retention.
- Hydrology: Seasonal water flow through the valley adds to its scenic and ecological significance.
Ecological and Cultural Significance
The Rift Valley and its surrounding region hold ecological and cultural importance:
- Biodiversity: Despite its arid environment, the valley hosts unique flora and fauna adapted to the plateau’s conditions.
- Agriculture: The fertile loess soil has historically supported farming communities, although soil erosion remains a challenge.
- Cultural Heritage: The Loess Plateau is steeped in history, with the valley providing a backdrop to ancient settlements and traditional Chinese agricultural practices.
Tourism and Research Opportunities
The Pinglu Rift Valley attracts geologists, ecologists, and tourists:
- Geological Research: The valley provides a natural laboratory for studying tectonic activity and erosion processes.
- Ecotourism: Visitors can experience the dramatic landscapes of the Loess Plateau, including the valley’s steep cliffs and expansive views.
- Cultural Exploration: Nearby villages offer a glimpse into the lives of communities shaped by this unique terrain.

Challenges and Conservation
The Rift Valley and the larger Loess Plateau face several challenges:
- Soil Erosion: The loess soil is prone to degradation, threatening the valley’s stability and nearby agriculture.
- Climate Change: Changing weather patterns may intensify erosion and alter the region’s hydrology.
Efforts are being made to address these issues, such as implementing soil conservation techniques and promoting sustainable land use.