Nikola Tesla, born on July 10, 1856, in the village of Smiljan, in what is now modern-day Croatia, remains one of history’s most remarkable inventors. Known for his visionary ideas and groundbreaking innovations, Tesla’s contributions laid the foundation for many technologies we rely on today. His work, particularly in electricity and wireless communication, shaped the modern world and continues to inspire countless scientists and engineers.
Early Life and Education
Tesla’s brilliance emerged at a young age. The son of a Serbian Orthodox priest and an inventive mother, Tesla displayed an exceptional aptitude for mathematics and engineering. In 1875, he enrolled at the Austrian Polytechnic in Graz, where he demonstrated exceptional focus and intellectual rigor. However, due to personal struggles and financial difficulties, Tesla left school in 1878, marking the beginning of his unconventional journey toward greatness.
Tesla’s Journey to America
In 1884, Tesla immigrated to the United States, bringing his boundless ideas to a land of opportunity. He briefly worked under the legendary inventor Thomas Edison, tasked with improving Edison’s direct current (DC) systems. However, the two inventors had a stark clash of personalities and ideas, leading Tesla to part ways with Edison and embark on his independent path.
The Birth of Alternating Current (AC)
Tesla’s most transformative contribution came with the development of the alternating current (AC) system. While Edison championed direct current, Tesla’s AC technology allowed electricity to travel over longer distances with greater efficiency. By 1887, Tesla’s inventions caught the attention of George Westinghouse, who recognized the potential of AC and partnered with Tesla.
This partnership became the cornerstone of the “War of the Currents”, a fierce rivalry between Tesla and Edison over the future of electricity distribution. Tesla’s AC system ultimately emerged victorious, powering homes, factories, and entire cities.
The Tesla Coil: A Leap Toward Wireless Technology
In 1891, Tesla invented the Tesla coil, a device capable of producing high-voltage, low-current electricity. This invention became an essential component in wireless communication systems and paved the way for advances in radio technology. Tesla envisioned a future where wireless transmission of energy could eliminate wires entirely, enabling a more interconnected world.
Pioneering Wireless Communication and Robotics
Tesla’s innovative thinking wasn’t limited to electricity. In 1898, he unveiled a radio-controlled boat, demonstrating the potential of wireless communication and robotics. This invention was decades ahead of its time, setting the stage for modern technologies like drones, remote controls, and even autonomous vehicles.
The Wardenclyffe Tower: Tesla’s Dream of Global Wireless Energy
Perhaps one of Tesla’s most ambitious projects was the Wardenclyffe Tower, constructed in 1901 on Long Island, New York. Tesla intended this structure to provide global wireless energy transmission, making electricity accessible to everyone. Despite its revolutionary vision, the project faced financial struggles and was abandoned in 1906.
This setback marked the beginning of Tesla’s declining fortunes, as funding for his grand ideas dwindled.
Tesla’s Later Years and Struggles
Though Tesla secured over 300 patents throughout his life, financial mismanagement and lack of commercial success left him in poverty during his later years. Living in modest hotel rooms in New York City, Tesla devoted much of his time to feeding pigeons, finding solace in their companionship.
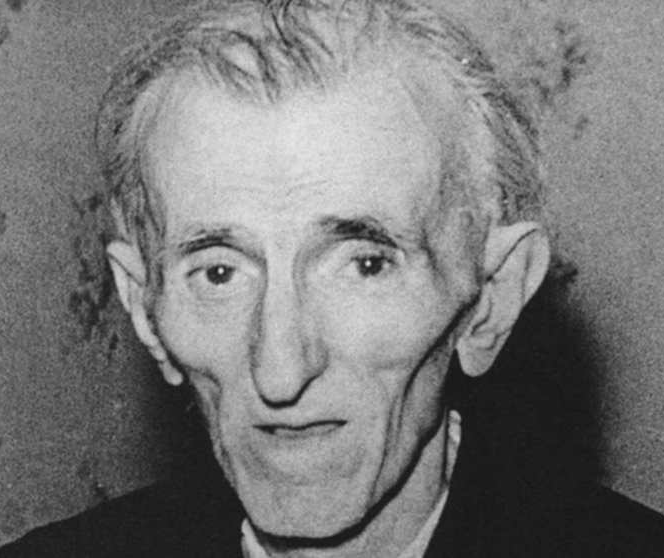
A poignant moment in Tesla’s life occurred on January 1, 1943, when the last photograph of him was taken, capturing a frail yet thoughtful man. Tesla passed away just six days later, on January 7, from a heart attack, at the age of 86.
Tesla’s Legacy: An Inspiration for the Future
Tesla’s legacy is one of visionary genius and relentless pursuit of progress. His work in electricity, wireless communication, and robotics laid the groundwork for innovations ranging from smart grids to space exploration. Though underappreciated during his lifetime, Tesla is now celebrated as a pioneer who transformed human life with his revolutionary ideas.
Modern companies and technologies, such as Tesla, Inc., continue to honor his name, driving advancements in renewable energy and autonomous vehicles. Tesla’s ability to dream beyond the limits of his time remains a beacon of inspiration, urging humanity to explore new frontiers.

1. What was Nikola Tesla’s most significant invention?
Tesla’s most significant invention was the alternating current (AC) system, which revolutionized electricity distribution by enabling efficient power transmission over long distances.
2. Why did Tesla leave Thomas Edison’s employment?
Tesla left Edison due to disagreements over compensation and fundamental differences in their approaches to technology, particularly their views on AC versus DC systems.
3. What was the purpose of the Wardenclyffe Tower?
The Wardenclyffe Tower was intended to provide wireless transmission of energy across the globe. Tesla envisioned a world where energy could be freely transmitted to everyone.
4. How did Tesla influence modern technology?
Tesla’s contributions laid the foundation for many technologies, including radio, robotics, wireless communication, and modern power grids. His visionary thinking continues to inspire contemporary innovation.
5. Why did Tesla face financial difficulties?
Despite his many patents, Tesla struggled with financial management and often lacked funding to commercialize his ideas. Many of his grand projects, like the Wardenclyffe Tower, were abandoned due to insufficient resources.
6. How is Tesla remembered today?
Tesla is celebrated as one of history’s greatest inventors. Institutions, technologies, and companies like Tesla, Inc., honor his name, ensuring his contributions remain central to the story of technological progress.